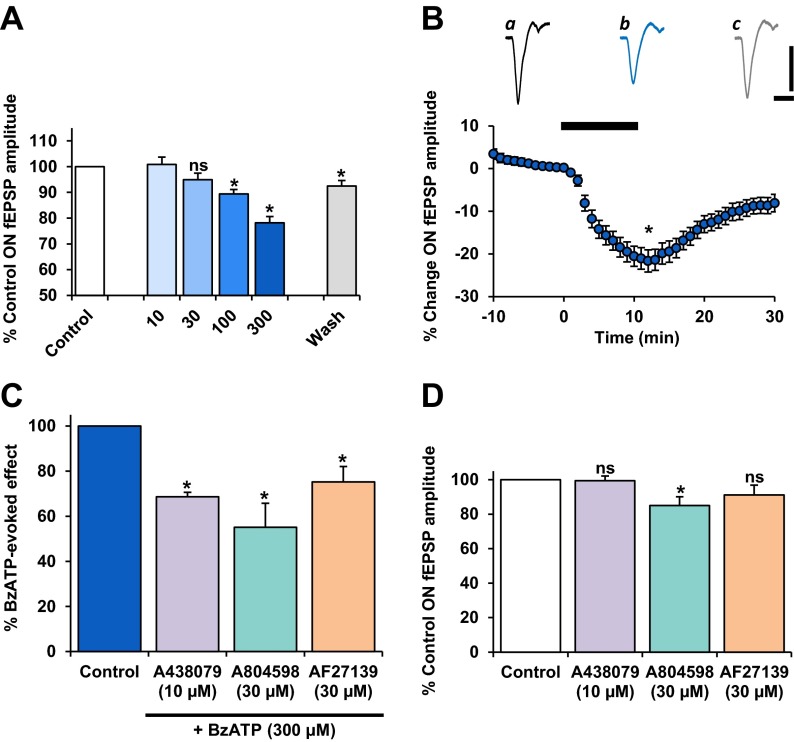
Fig. 3.
The effect of BzATP on the light-evoked ON-fEPSP. Responses are pharmacologically isolated, NMDAR-mediated. BzATP was applied (10 min) at concentrations of 10 (n = 2), 30 (n = 6), 100 (n = 6) and 300 μM (n = 21). Values are mean ± SEM percentage of pre-treatment control fEPSP peak amplitude. a BzATP elicited a concentration-related reduction of the ON-fEPSP. Washout of BzATP (300 μM) induced recovery of the ON-fEPSP. b Time course plot shows the effect of BzATP (300 μM) on the ON-fEPSP. Plotted values are mean ± SEM percentage change in fEPSP peak amplitude, relative to pre-treatment control. Representative traces (120 s averages) illustrate the effect of BzATP (300 μM) on the ON-fEPSP. a Control, b BzATP (300 μM), c wash. Scale bars = 400 ms, 20 μV. c Actions of selective P2X7R antagonists on the BzATP-induced suppression of the ON-fEPSP. The selective P2X7R antagonists, A438079 (n = 6), A804598 (n = 7) or AF27139 (n = 6), significantly attenuated the BzATP (300 μM)-mediated reduction of the ON-fEPSP. All three compounds exhibited similar potency in blocking P2X7R function at the concentrations tested. Note that in the presence of all antagonists, a large residual effect on the ON-fEPSP persisted with BzATP application. d Direct actions of selective P2X7R antagonists on the NMDAR-mediated ON-fEPSP. The ON-fEPSP was significantly reduced in the presence of A804598 (n = 7) but not by A438079 (n = 6) or AF27139 (n = 6) at the concentrations tested. ns not significant; *P < 0.05, compared to control