Fig. 6.
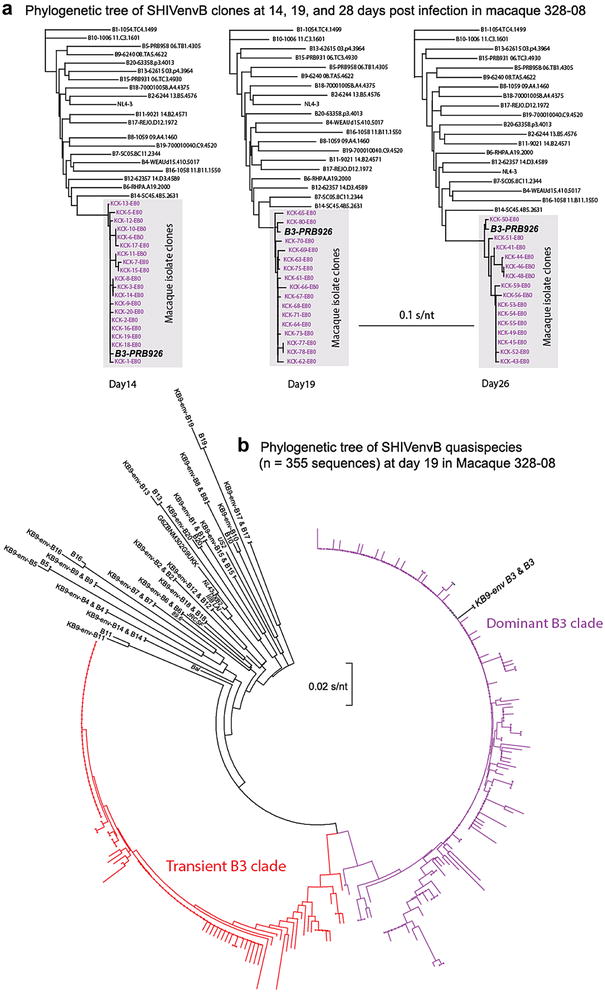
Sequence analyses from plasma of the infected macaques. HIV RNA was extracted from plasma collected from the m328-08 and then subjected to RT-PCR amplification, TOPO cloning, and sequence analyses of 15–19 clones from days 14, 19, and 26 post inoculation. A 480 nt gp120 coding region (C2-V3) of the m328-08 clones were aligned with all the SHIVenv_B clones within the inoculating pool using CluxtalX. Neighbor joining trees were constructed using FigTree and presented in (a). Only a single SHIVenv_B3 clone established and maintained infection in macaque 328-08. The RT-PCR amplified HIV-1 gp120 product derived from ~10,000 RNA copies at day 19 was subjected to 454 pyrosequencing. The C2-V3 sequences from day 19, the 16 SHIVenv_B sequences from the inoculating pool, and a set of subtype B reference sequences were aligned using Bayesian algorithm (Beast) [73] and trees were constructed using a maximum likelihood method. The tree presented in b was drawn with FigTree v1.4 (http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree)
