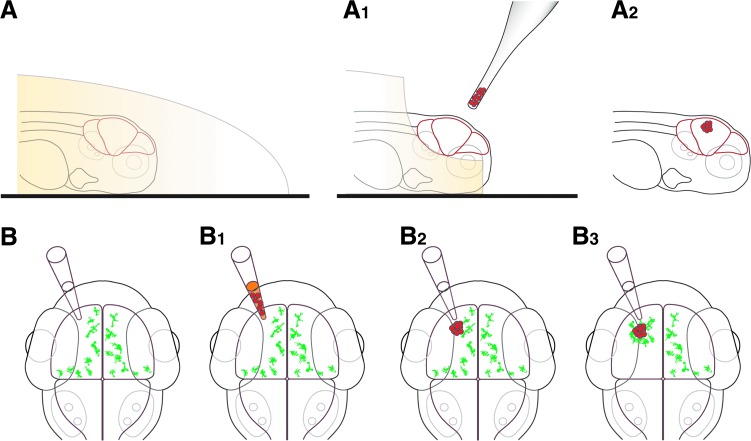
FIG. 1.
Zebrafish larval xenograft. (A–A2) Schematic representation of the xenograft technique, lateral view. (A) Zebrafish larvae were mounted in low-melting point agarose (beige). (A1) Larval heads were released from the low-melting point agarose to allow cell transplantation into the brain. (A2) Cells (red) were transplanted into the optic tectum. (B–B3) Schematic representation of the xenograft technique, dorsal view. Cells (red) were transplanted into the left optic tectum, stimulating a microglia (green) response (depending on cell type). The right optic tectum served as an internal control.