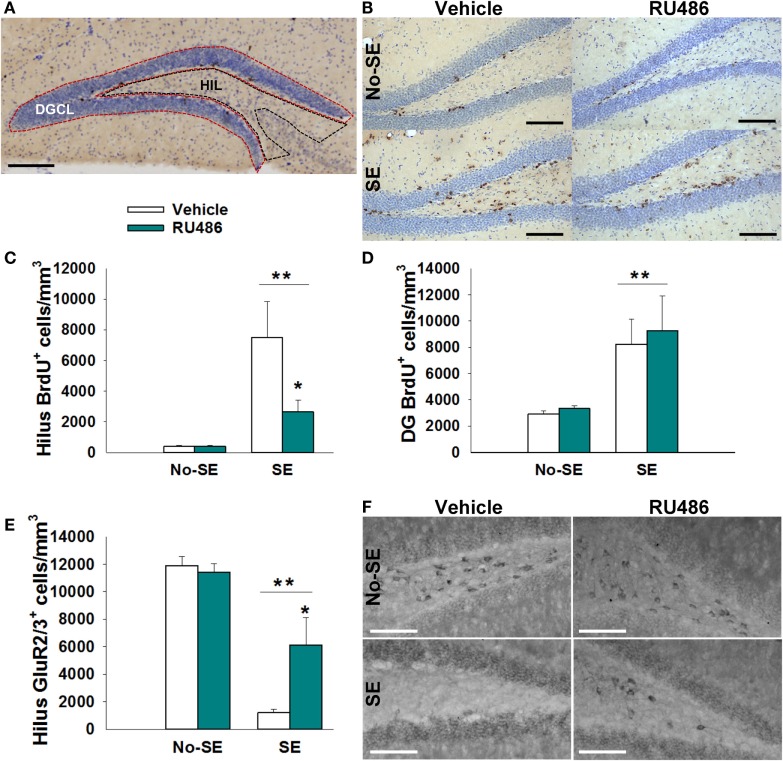
Figure 2.
RU486 reduced mossy cell loss and hilar BrdU+ neurons in the hippocampus of post-SE mice. (A) Micrograph depicting the regions analyzed: dentate granule cell body layer (DGC) and the hilus (HIL). Scale bar = 200 μm. (B) Micrograph showing examples of BrdU+ staining. Scale bars = 100 μm. (C) SE leads to an increased number of BrdU+ cells in the dentate hilus (**p < 0.01 main effect of SE). RU486 treatment reduced the number of BrdU+ cells in the dentate hilus of post-SE mice relative to vehicle-treated post-SE mice (*p < 0.05, RU486 different from vehicle within SE). (D) SE leads to an increase in BrdU+ cells in the dentate gyrus relative to control mice (**p < 0.01 main effect of SE). (E) SE leads to loss of GluR2+ cells in the dentate hilus relative to control mice (**p < 0.01, main effect of SE). RU486 treatment preserves greater numbers of GluR2+ cells in the dentate hilus of post-SE mice relative to their vehicle-treated counterparts (*p < 0.05, RU486 different from vehicle within SE). (F) Micrograph depicting GluR2 immunohistochemistry in the dentate hilus. Scale bars = 100 μm. All data presented as mean ± SEM, n = 6–8 mice.