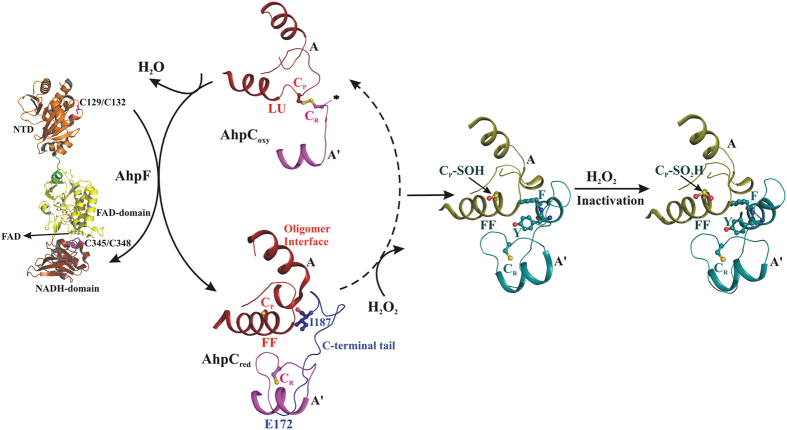
Figure 1. The catalytic cycle of 2-Cys Prxs.
The basic functional dimeric unit of 2-Cys Prxs and their active site region is shown. During peroxide reduction, the reduced CP assumes the FF conformation and reacts with H2O2 to form a CP-SOH intermediate. This local unfolding of the active site enables the formation of a disulphide bond with the CR located in the C-terminal tail of adjacent subunit. AhpC is then reduced by AhpF to its FF conformation for future catalytic cycles, with AhpF being oxidized in this process. AhpF is regenerated with the utilization of NADH molecules for further catalytic cycles. In comparison, human Prx is stabilized in the FF active site conformation even after the formation of the intermediate CP-SOH form, which eventually promotes over-oxidation.