Figure 4. Hyperlipidemia leads to Akt activation.
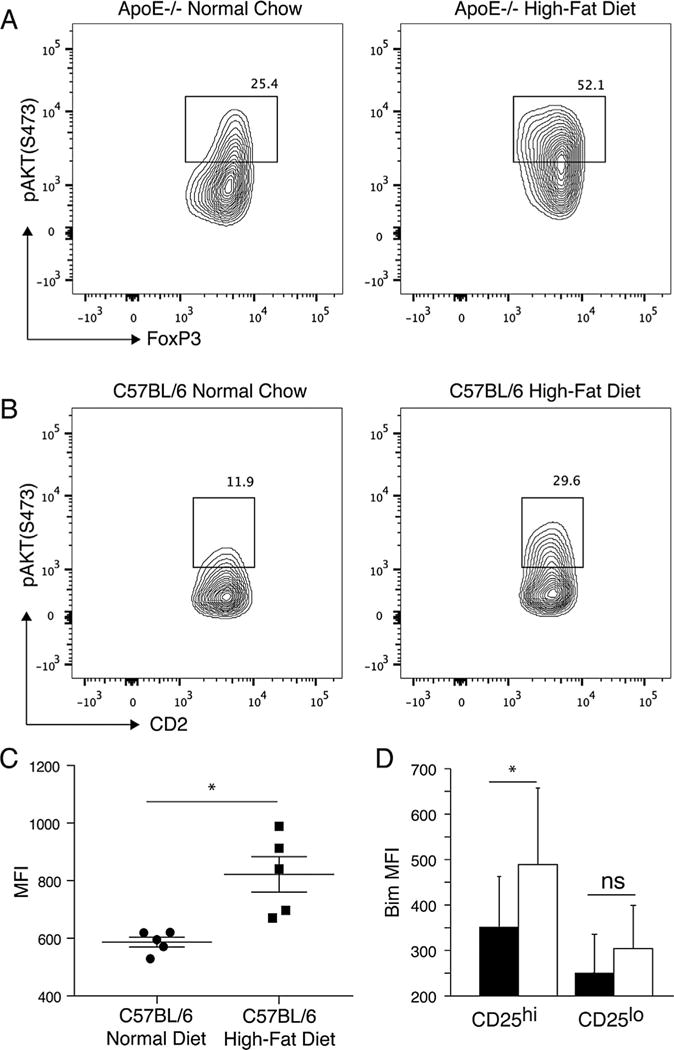
(A) Phospho-Akt levels in ApoE−/− controls fed normal chow and ApoE−/− mice fed a high-fat diet. ApoE−/− mice were fed either high-fat diet or normal chow for 10 weeks. Splenocytes were examined for expression of CD4, FoxP3 and phospho-AKT directly ex vivo. Shown gated on CD4+FoxP3+ lymphocytes. (B) Phospho-Akt levels in C57BL/6 controls fed normal chow and C57BL/6 mice fed a high-fat diet. C57BL/6 mice were fed either high-fat diet or normal chow for 10 weeks. Splenocytes were examined for expression of CD4, hCD2 and phospho-AKT directly ex vivo. Shown gated on CD4+CD2+ lymphocytes. (C) Median fluorescent intensity (MFI) of phospho-Akt levels in C57BL/6 controls fed normal chow and C57BL/6 mice fed a high-fat diet. (D) Expression of Bim in CD4+FoxP3+ cells expressing high levels (CD25hi) or low levels (CD25lo) of CD25 in ApoE−/− mice fed a high-fat diet for 4 weeks (black bars) or age-matched C57BL/6 mice fed normal chow (white bars) are shown. Combined results of three experiments are shown. Asterisk indicates p < 0.05. ApoE, apolipoproteinE; CFSE, carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester; FoxP3, forkhead box P3.
