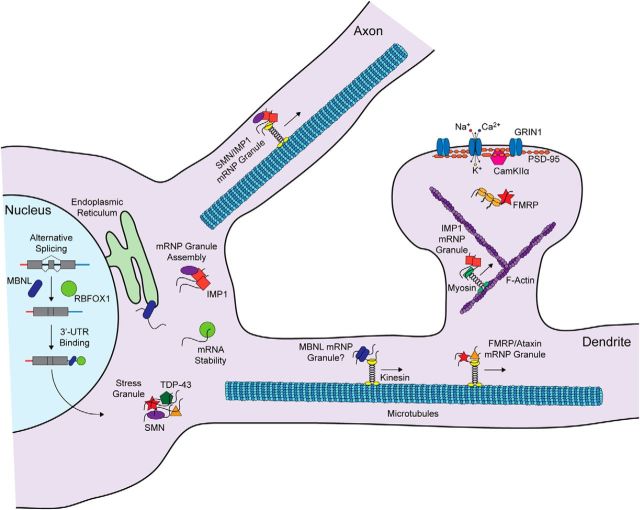
Figure 1.
Spatiotemporal regulation of RNA processing and local translation in neurons by RNA-binding proteins. In the nucleus, MBNL and RBFOX proteins regulate splicing and bind 3′-UTR sequences. Both proteins coregulate many transcripts. In the cytoplasm, MBNL binds to the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) where it facilitates the synthesis of membrane proteins, and also associates with the cytoskeleton to regulate mRNA localization. The cytoplasmic isoform of RBFOX1 regulates mRNA stability. Several RNA-binding proteins (e.g., FMRP, Ataxin, TDP-43, and Smn) are associated with stress granules. FMRP and Imp1 regulate mRNA granule transport by kinesin and local translation in dendritic spines. Imp1 also regulates mRNA localization in axons, and Smn plays a role in the assembly of Imp1 RNA transport granules. RNA localization and translation in spines may involve myosin motor and anchoring to F-actin. Locally synthesized proteins include glutamate receptor subunits, components of the postsynaptic density, and signaling proteins.