Figure 2.
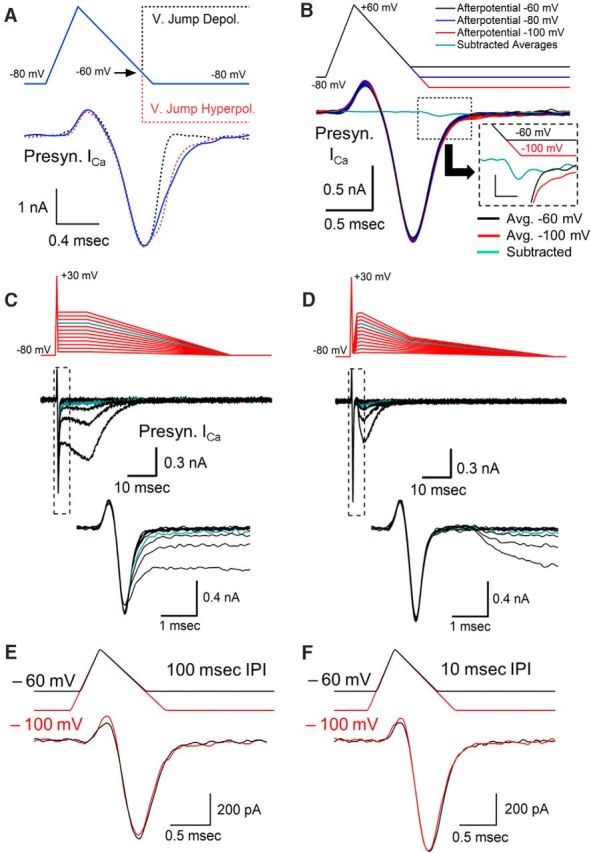
Effects of afterpotentials after an AP-like stimulus. A, Depolarizing voltage jumps to +60 mV and hyperpolarizing voltage jumps to −150 mV were used during an AP-like stimulation to determine the amount of calcium channel activity that is present at the time that our standard afterdepolarization occurs. B, Responses to AP-like stimulation with afterpotentials at −60, −80, and −100 mV. Responses are from a representative cell, with each value tested 10 times. Cyan trace shows the average of 10 calcium channel responses to a −60 mV afterpotential subtracted from the average of 10 responses to a −100 mV afterpotential. Inset shows subtracted average trace at higher resolution with the stimulus bar shifted 0.15 ms to adjust for the delay between the stimulus and the response. Inset scale bars, 50 pA, 0.3 ms. C, Effects of ADPs on presynaptic voltage-gated calcium current over a range of −75 to −20 mV tested in 5 mV increments. Cyan line (−35 mV) indicates afterpotential amplitude where calcium current is first affected. Bottom trace shows calcium current at higher temporal resolution. D, Effects of separating the afterpotential from the AP waveform by returning the membrane potential to −75 mV for 1 ms followed by afterpotentials over a range of −75 to −20 mV tested in 5 mV increments. Cyan line (−35 mV) indicates potential amplitude where calcium channels begin to respond. E, Changing the membrane potential has only a small effect on the presynaptic calcium current generated by an AP-like stimulation. Overlay of two responses from a 10 Hz stimulation train. The membrane potential was held at −60 mV (black trace) or −100 mV (red trace) for 100 ms before the AP-like stimulus. A small difference in the transient upward current is apparent between the responses at −60 mV compared with −100 mV, consistent with differences that would be produced by a gating charge. Trains were <0.5 s in duration. F, Overlay of two responses occurring during a 100 Hz stimulus train. The membrane potential was at −60 mV (black trace) or −100 mV (red trace) for 10 ms before the AP-like stimulus.
