Figure 5.
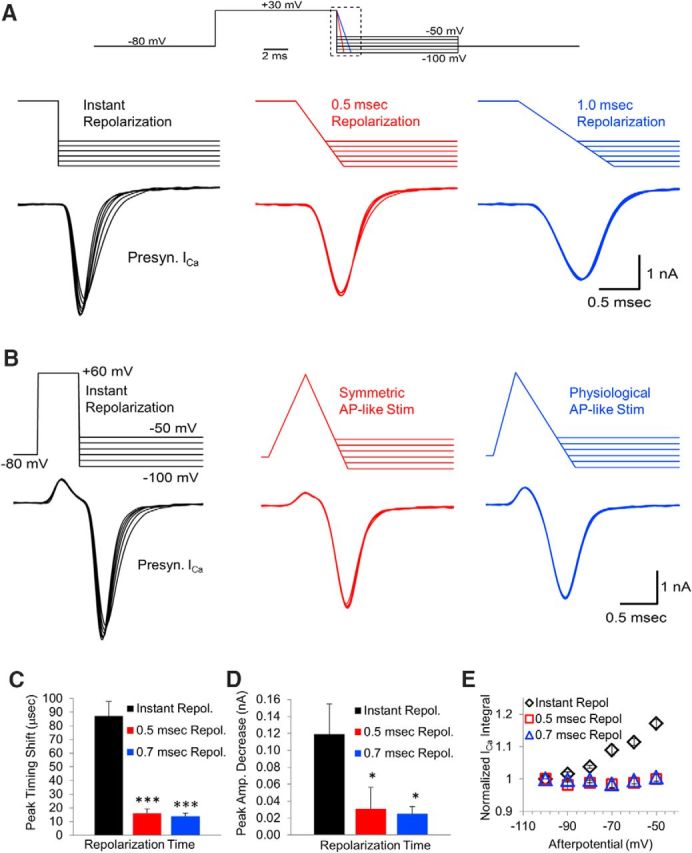
Ramped repolarization acts to reduce or eliminate effects of afterpotentials. A, Presynaptic calcium channels were activated by a 10 ms depolarization to +30 mV and then repolarized instantly (left trace), over 0.5 ms (center trace), or over 1.0 ms (right trace). These repolarizations ended with afterpotentials between −50 and −100 mV in 10 mV increments. B, Timing of the peak of the presynaptic calcium channel response to afterpotentials at −100 and −50 mV after an instant repolarization versus AP-like stimulation with 0.5 or 0.7 ms repolarization. C, Time from the onset to the peak amplitude of the calcium channel response to afterpotentials at −100 and −50 mV after an instant repolarization versus 0.5 or 0.7 ms repolarization. D, Peak amplitude of the calcium channel response to afterpotentials at −100 and −50 mV after an instant repolarization versus 0.5 or 0.7 ms repolarization. E, Normalized integral of the calcium channel response to afterpotentials after an instant repolarization, a 0.5 ms repolarization, or a 0.7 ms repolarization.
