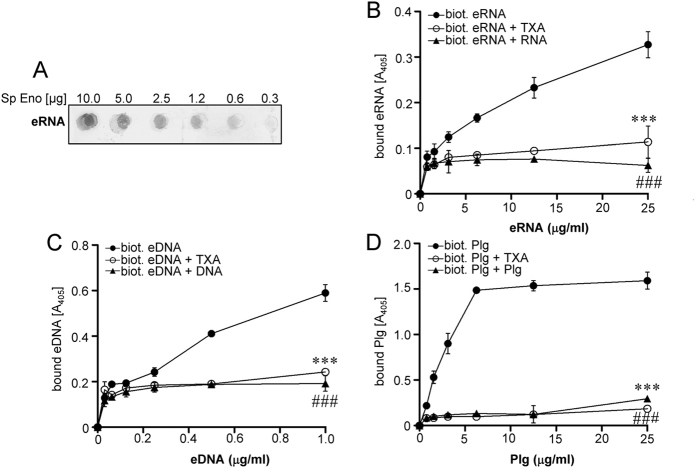
Figure 2. Extracellular RNA interacts with pneumococcal Eno.
(A) Different amounts of recombinant S. pneumoniae Eno (0.32, 0.65, 1.25, 2.5, 5 and 10 μg) were spotted on a nitrocellulose membrane. The Eno/eRNA interaction was tested using biotinylated eRNA and peroxidase-coupled streptavidin. (B) Five μg of S. pneumoniae Eno were immobilized onto a microtiter plate and incubated with different concentration of biotinylated eRNA (●) in the presence or absence of unlabeled eRNA (▲) and tranexamic acid (TXA) (○). (C) Eno was incubated with different concentration of biotinylated eDNA (●) in the presence or absence of unlabeled eDNA (▲) and tranexamic acid (TXA) (○). (D) Eno was incubated with different concentrations of biotinylated plasminogen (Plg) (●) in the presence or absence of unlabeled Plg (▲) and TXA (○). Data represent mean values ± SEM; n = 3; ###p ≤ 0.001; ***p ≤ 0.001 vs biotinylated eRNA/eDNA/Plg (●).