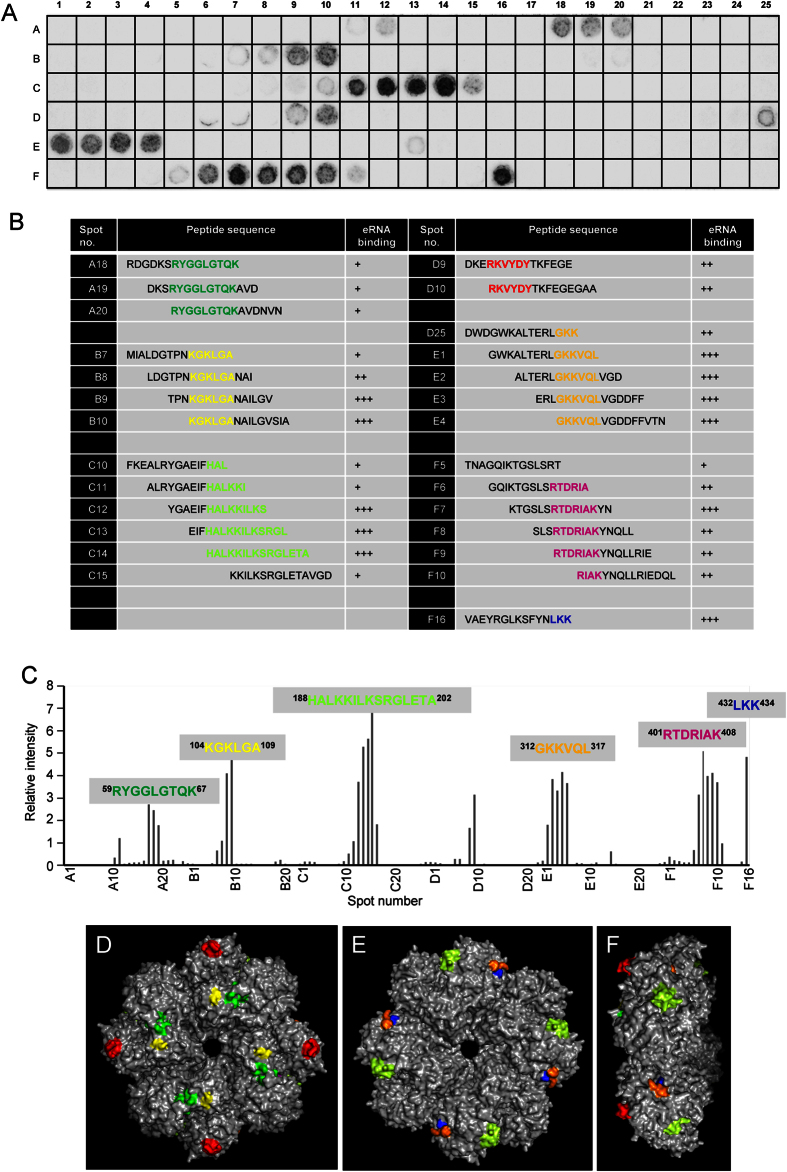
Figure 4. Identification and localization of eRNA-binding regions of Eno protein.
(A) The entire pneumococcal Eno protein was divided into 141 overlapping peptides, each consisting of 15 amino acids, with an offset of three amino acids. The synthetic peptides were assayed for their ability to bind eRNA using dot blot analysis. (B) Sequences of spots (A18-A20, B7-B10, C10-C15, D9-D10, D25-E4, F5-F10 and F16) and the binding reactivity to biotinylated RNA. +, weak binding; ++, moderate binding; +++, strong binding. (C) Densitometry of (A). (D–F) Extracellular RNA-binding motifs on the surface of the pneumococcal Eno octamer. Six eRNA-binding regions in the Eno octamer are depicted in green (59RYGGLGTQK67), yellow (104KGKLGA109), light green (188HALKKILKSRGLETA202), orange (312GKKVQL31), magneta (401RTDRIAK408) and blue (432LKK434). Front view (D), backside view (E) and side view (F). Internal Plg-binding motif of Eno (248FYKERKVY256) is depicted in red. The figure was generated using PyMol (DeLano Scientific LLC).