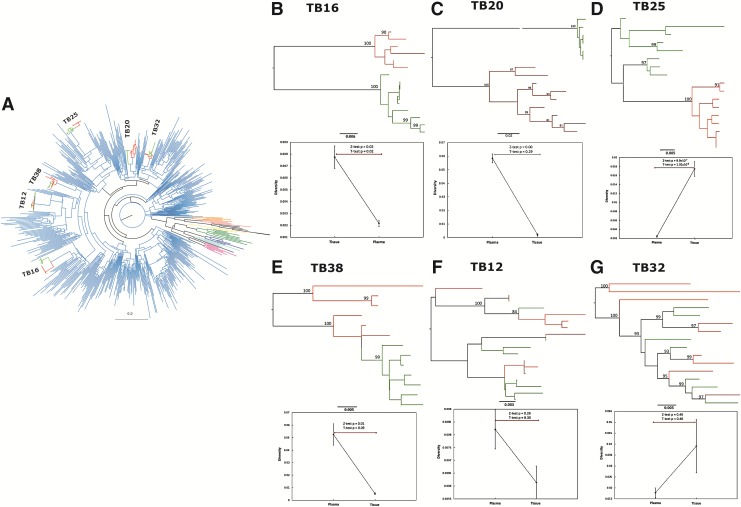
FIG. 1.
(A) A maximum likelihood tree of clonal plasma (red) and tissue-derived (green) sequences from individual patients clustering within the subtype C lineages (blue). Reference sequences of subtypes A (pink), B (purple), D (light blue), F (dark green), G (black), H (orange), J (salmon), and K (yellow) are also represented. The phylogenetic reconstruction was performed in RaxML using the HKY85 model with gamma distribution. (B–G) Phylogenetic reconstructions illustrating maximum likelihood trees constructed in RaxML of individual patient plasma-derived (red) and tissue-derived (green) sequences with branch support indicated are represented. (B–E) Two distinct patterns of clustering are observed where monophyletic clustering is shown [(B) TB16; (C) TB20; (D) TB25; (E) TB38)] and intermixing of variants is illustrated [(F) TB12 and (G) TB32]. The panels below each phylogenetic tree are graphic representations of intracompartment diversity measures as estimated in DIVEIN, which illustrates the median diversity and IQR. Two-sample diversity tests (T) were conducted and illustrated are p-values derived from z-tests and t-tests comparing intracompartment diversity of plasma-derived with tissue-derived sequences.