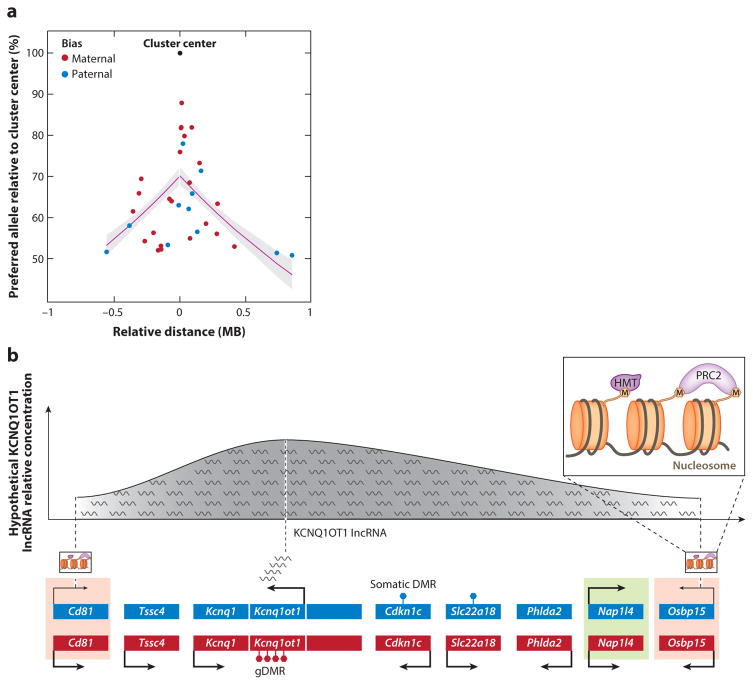
Figure 7.
Mechanistic models of parentally biased expression. (a) The decay of parental bias of imprinted genes as a function of their relative linear genomic distance from an imprinted cluster center (which is defined as the location of the monoallelically expressed imprinted genes in the cluster) in the cerebellum. The regression line is shown in magenta, and the gray shading indicates corresponding standard errors (Perez et al. 2015). (b) Known mechanisms of genomic imprinting in the mouse Kcnq1 imprinted cluster and their potential extrapolation to mechanisms of parental biases. The Kcnq1 intergenic, maternally methylated gDMR induces paternal-specific expression of Kcnq1ot1, an lncRNA that orchestrates imprinting of multiple genes at both ends of this cluster (Mancini-Dinardo et al. 2006, Terranova et al. 2008). In the placenta, genes closer to the gDMR, such as Cdkn1c, are monoallelically expressed in a DNA methylation–dependent manner (indicated by filled hexagons on top of gene bodies), whereas genes at the cluster periphery, such as Cd81 and Osbpl5, exhibit DNA methylation–independent maternal biases (red shading) (Lewis et al. 2004, Umlauf et al. 2004). Another peripheral gene, Nap1l4, is biallelically expressed ( green shading). Imprinting in these maternally biased genes is dependent on interactions between their respective promoters and Kcnq1ot1 transcripts, which recruit HMTs and PRC2, forming a contracted nuclear domain (Pandey et al. 2008, Terranova et al. 2008). Importantly, KCNQ1OT1 lncRNA does not interact with the Nap1l4 promoter. We suggest a potential model explaining parentally biased expression in this cluster (depicted on top) where the effective concentration or activity of the KCNQ1OT1 lncRNA across the length of the cluster may exhibit a normal distribution centered in its transcriptional site that decreases gradually toward the ends. In this model, the differences in KCNQ1OT1 lncRNA concentration or activity may explain its different actions in central and peripheral genes. Abbreviations: gDMR, germ-line differentially methylated region; HMT, histone methyltransferase; lncRNA, long noncoding RNA; PRC2, polycomb repressive complex 2.