Figure 5.
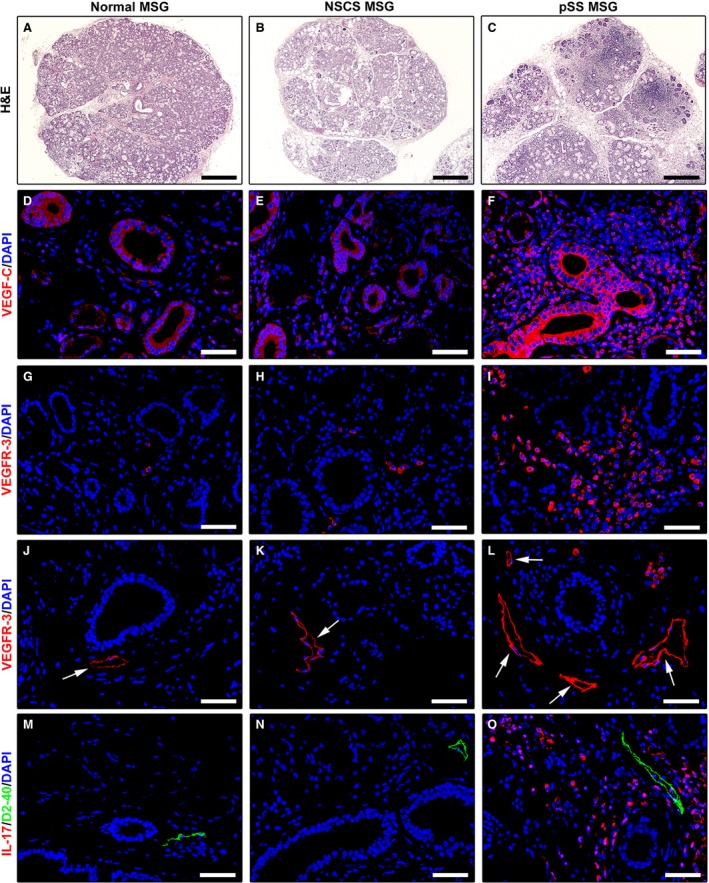
Increased expression of lymphangiogenic mediators in minor salivary glands (MSGs) from patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome (pSS). (A, D, G, J and M) Normal MSGs. (B, E, H, K and N) MSGs from non‐specific chronic sialadenitis (NSCS). (C, F, I, L and O) MSGs from pSS. (A–C) Hematoxylin and eosin staining. pSS MSGs display periductal inflammatory aggregates (foci) replacing the secretory units. (D–F) Immunofluorescence staining for VEGF‐C (red) with 4′,6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole (DAPI, blue) counterstain for nuclei. Faint expression of VEGF‐C is detected in normal and NSCS MSGs (D and E). In pSS MSGs, VEGF‐C is strongly expressed in ductal epithelial cells, microvessels and periductal inflammatory cells (F). (G–L) Immunofluorescence staining for VEGF receptor (VEGFR)‐3 (red) with DAPI (blue) counterstain. Numerous VEGFR‐3+ infiltrating mononuclear cells are present in pSS MSGs (I). Both in normal and NSCS MSGs, lymphatic capillaries (arrows) show weak VEGFR‐3 positivity (J and K). VEGFR‐3 expression is strongly increased in lymphatic capillaries (arrows) of pSS MSGs (L). (M–O) Double immunofluorescence staining for interleukin (IL)‐17 (red) and the lymphatic vessel marker podoplanin (D2‐40, green) with DAPI (blue) counterstain. No IL‐17 expression can be detected either in normal or NSCS MSGs (M and N). Numerous IL‐17+ inflammatory cells are present around lymphatic vessels in pSS MSGs (O). Original magnification: ×5 (A–C), ×40 (D–O). Scale bar: 400 μm (A–C), 50 μm (D–O).
