Fig 1. Endoglycan and Podocalyxin localization during lumen formation.
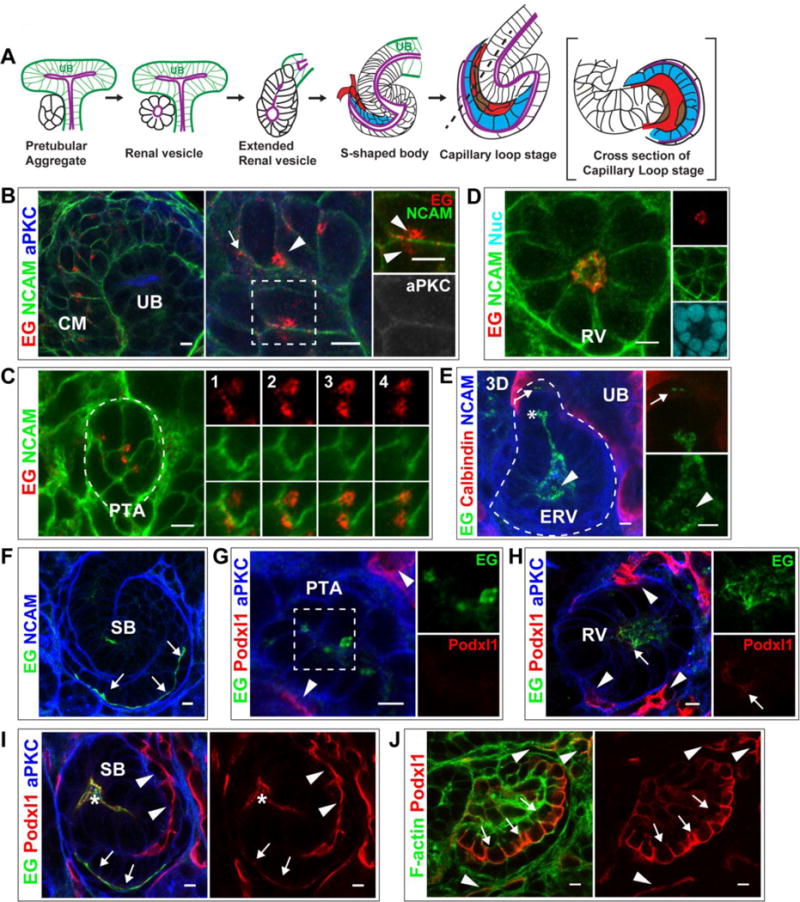
(A) General schematic of lumen formation in developing nephrons. The cap mesenchyme (not shown) compacts to form a pretubular aggregate (PA). The PA becomes a polarized, epithelial sphere called the renal vesicle (RV) containing a central lumen (purple). The RV becomes an extended structure, then forms the s-shaped body (SB), whose lumen is continuous with the ureteric bud (UB) lumen (purple). As the SB elongates, endothelial (red) and mesangial (brown) precursors invade the SB cleft and the SB “tail” forms a primordial glomerulus known as the capillary loop stage. Podocyte precursors are indicated (blue).
(B–F) Localization of Endoglycan (EG) in P0 kidney in CM (B), PA (C), and RV (D) stages. EG localizes largely to punctate structures in CM and PA, then relocalizes to the nascent nephron lumen. NCAM marks the plasma membrane in CM and PA and becomes restricted to the lateral surfaces in RVs. aPKC marks apical, luminal surfaces (B). In extended RVs (E), EG localizes to the lumen, including the leading portion (asterisks), and is in contiguous cells prior to lumen formation (arrow). EG also localizes to intraluminal structures in the widened lumen (arrowhead). Calbindin marks the adjacent UB. (F) EG is apical (and intraluminal) in the SB stage, including the apical surface of podocyte precursors (arrows).
(G–J) Localization of Podocalyxin (Podxl1) in P0 kidney shows it is absent from CM (not shown) and PA (G), but is present at low levels in RV (H, arrow). Podxl1 also localizes to endothelia (H, arrowheads), where levels are higher. (I) Podxl1 levels increase at the SB stage, where it is apical/luminal (asterisks indicate mid-SB and arrows indicate proximal SB where podocyte precursors reside). (J) Further increase in Podxl1 is observed in early glomeruli at the apical surface of immature podocytes (arrows) and in endothelia (arrowheads). Results are representative of 3 experiments. Scale bars: 5 μm.
