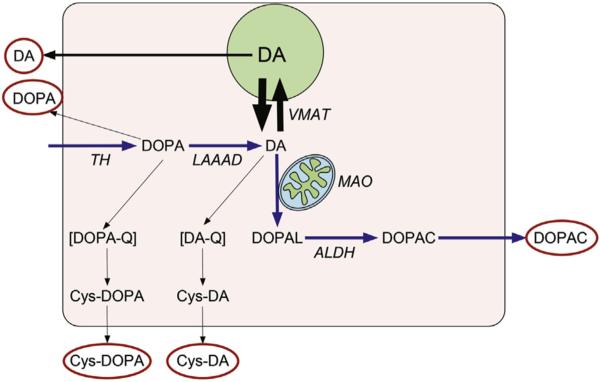
Fig. 1. Parent and Cys-catechols.
Cytoplasmic dopamine (DA) synthesis depends on conversion of tyrosine to 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) via tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and decarboxylation of DOPA via L-aromatic-amino-acid decarboxylases. Cytoplasmic DA is taken up into vesicles via the vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT), is metabolized by monoamine oxidase (MAO), or oxidizes spontaneously to form cysteinyl-dopamine (Cys-DA). MAO converts DA to toxic 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde (DOPAL), which is detoxified by aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) to form 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC). DOPA oxidizes spontaneously to cysteinyl-DOPA (Cys-DOPA) and DA to Cys-DA. Red ovals indicate CSF analytes assayed in this study. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)