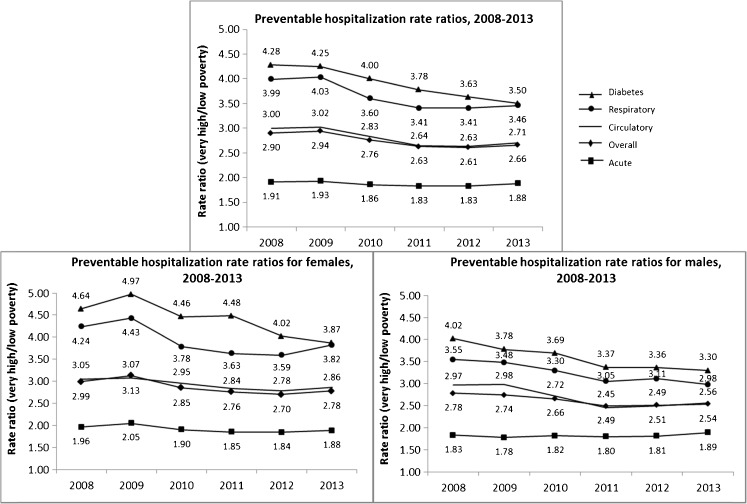
FIG. 3.
Preventable hospitalization rate ratios for New York City residents living in very high poverty neighborhoods versus low poverty neighborhoods, overall and by sex, 2008–2013. Source: NYS Dept of Health SPARCS 2008–2013 (updated July 2014 for 2008–2010, December 2014 for 2011–2012, June 2015 for 2013). Preventable Hospitalizations based on AHRQ PQI version 4.5a, updated 2014. Population data for rates from NYCDOHMH interpolated intercensal Population Estimates, modified from US Census Bureau, using poverty groups from the American Community Survey 2009–2013. Neighborhood poverty (based on ZIP codes) defined as percent of residents with incomes below 100 % of the Federal Poverty Level, per American Community Survey, 2008–2013. ZIP codes with zero people for whom poverty status could be determined are excluded from the analysis. Rates per 100,000 are age-adjusted to the US 2000 Standard Population. Trends in rate ratios not statistically significant for acute conditions (overall, for males and for females), and not statistically significant for females for respiratory and overall preventable hospitalizations.