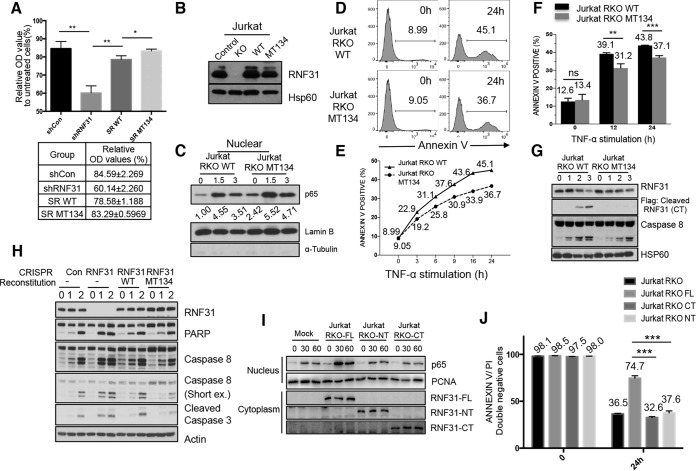
FIG 7.
A cleavage-resistant RNF31 mutant enhances resistance to apoptosis. (A) MTT analysis of lysates from control KD (shCon), RNF31 KD (shRNF31), WT RNF31-reconstituted RNF31 KD (SR WT), and cleavage-resistant RNF31 mutant-reconstituted RNF31 KD (SR MT134) HeLa cells treated with TNF-α (100 ng/ml). Single and double asterisks indicate significant differences at P values of <0.05 and <0.01, respectively. OD, optical density. (B) WB analysis of control, RNF31-deficient, RKO-WT, and RKO-MT134 Jurkat cells. (C) WB analysis of nuclear lysates from RKO-WT and RKO-MT134 Jurkat cells treated with TNF-α (20 ng/ml). (D) Flow cytometry analysis of Jurkat RKO-WT and Jurkat RKO-MT134 cells treated with TNF-α (200 ng/ml) for 24 h. The percentage of annexin V-stained cells is given in each panel. (E) Sensitivities to apoptosis of Jurkat RKO-WT and Jurkat RKO-MT134 cells treated with TNF-α (200 ng/ml) for the indicated periods. (F) Flow cytometry analysis of Jurkat RKO-WT and Jurkat RKO-MT134 cells treated with TNF-α (200 ng/ml) plus cycloheximide for the times shown. ns, not significant. Double and triple asterisks indicate significant differences at P values of <0.01 and <0.001, respectively. (G) WB analysis of RKO-WT and RKO-MT134 Jurkat cells stimulated with TNF-α (50 ng/ml). (H) WB analysis of control, RNF31-deficient, RKO-WT, and RKO-MT134 Jurkat cells treated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml) and CHX (10 μg/ml). (I) WB analysis of Jurkat RKO-Mock, Jurkat RKO-FL, Jurkat RKO-NT, and Jurkat RKO-CT cells stimulated with TNF-α (10 ng/ml). (J) Flow cytometry analysis of Jurkat RKO, Jurkat RKO-FL, Jurkat RKO-CT, and Jurkat RKO-NT cells treated with TNF-α (100 ng/ml) for 24 h.