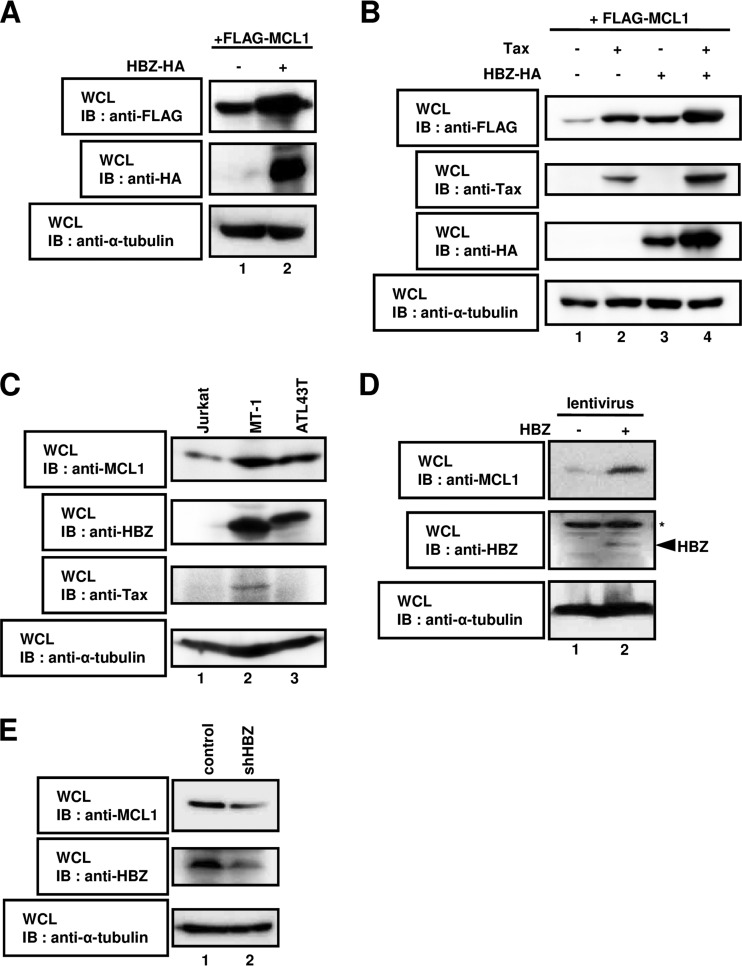
FIG 1.
HBZ regulates the stability of the MCL1 protein. (A) HEK293T cells were cotransfected with 1 μg of a plasmid expressing FLAG-MCL1 with (lane +) or without (lane −) 3 μg of a plasmid expressing HBZ-HA. After 36 h, cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with anti-FLAG, anti-HA, or anti-α-tubulin antibodies. (B) HEK293T cells were cotransfected with 0.5 μg of a plasmid expressing FLAG-MCL1 with (lanes +) or without (lanes −) 2.5 μg of a plasmid expressing Tax and HBZ-HA. After 36 h, cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with anti-FLAG, anti-Tax, anti-HA, and anti-α-tubulin antibodies. (C) Lysates prepared from Jurkat, MT-1, and ATL43T cells were subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-MCL1, anti-HBZ, anti-Tax, and anti-α-tubulin antibodies. (D) The lentivirus-based expression system was used to create Jurkat cell lines that carried the empty vector (lane 1) or that stably expressed HBZ (lane 2). Whole-cell lysates were prepared and subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-MCL1, anti-HBZ, and anti-α-tubulin antibodies. *, nonspecific bands. (E) SLB-1 cells were transduced with lentiviral particles containing shRNA targeting luciferase (control; lane 1) or HBZ (shHBZ; lane 2). Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-MCL1, anti-HBZ, and anti-α-tubulin antibodies. WCL, whole-cell lysates; IB, immunoblotting.