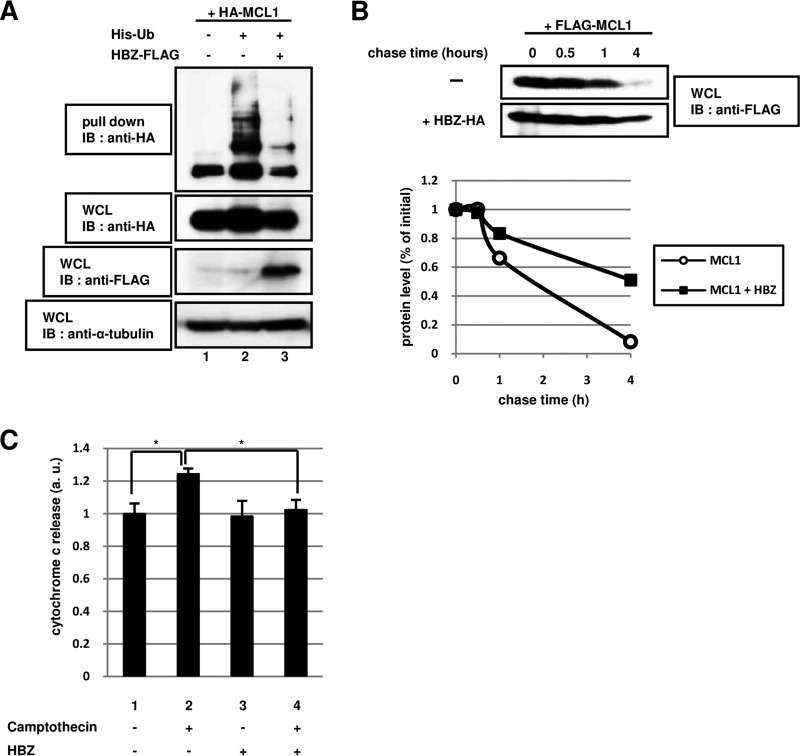
FIG 2.
The degradation of MCL1 by the ubiquitin-dependent pathway is controlled by HBZ. (A) NIH 3T3 cells were transfected (+) or not transfected (−) with 2 μg of pcDNA3-HA-MCL1 (HA-MCL1), pcDNA3-His-Ub (His-Ub), and pcDNA3-HBZ-FLAG (HBZ-FLAG), as indicated. After 24 h, the cells were treated with 20 μM MG132 (a proteasome inhibitor) for 15 h. Following purification with Ni-NTA beads, bound proteins were detected by immunoblotting with anti-HA antibody. Total protein levels in whole-cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-HA, anti-FLAG, and anti-α-tubulin antibodies. (B) HEK293T cells were transfected with 1 μg of a plasmid expressing FLAG-MCL1 with (+) or without (−) 3 μg of a plasmid expressing HBZ-HA. After 36 h, the cells were treated with 50 μM cycloheximide (a protein synthesis inhibitor) and then collected at the indicated times. Cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting using an anti-FLAG antibody. The intensity of each band was quantified and graphed. (C) HeLa cells were transfected (+) or not transfected (−) with 2 μg of pcDNA3-HBZ (HBZ). After 36 h, the cells were treated with 100 μM camptothecin for 6 h. The level of cytochrome c released was measured using a cytochrome c ELISA kit. Each value represents the mean from three independent experiments ± SE (*, P < 0.05). WCL, whole-cell lysates; IB, immunoblotting; a.u., arbitrary units.