FIG 1.
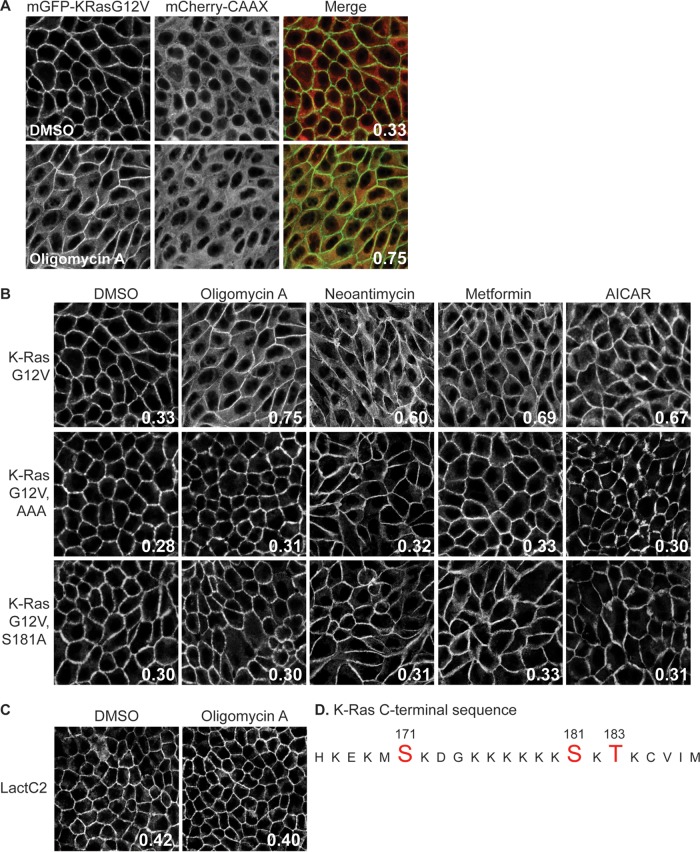
AMPK activation mislocalizes K-RasG12V from the PM as a result of C-terminal phosphorylation. (A and B) MDCK cells stably coexpressing mCherry-CAAX, a general endomembrane marker (67), and mGFP–K-RasG12V, mGFP–K-RasG12V T171A, S181A, or S183A (AAA), or mGFP–K-RasG12V S181A were treated with 2.6 nM oligomycin A, 5.2 nM neoantimycin, 1 mM metformin, or 1 mM AICAR for 48 h, and cells were fixed and imaged using a confocal microscope. K-Ras mislocalization from the PM was quantified as the colocalization of mGFP–K-RasG12V and mCherry-CAAX using Manders coefficients. (A) A representative image showing the green (mGFP) and red (mCherry) channels used to calculate the Manders coefficients. (B) The Manders coefficient is shown on each representative image of drug-treated cells. (C) MDCK cells stably coexpressing mCherry-CAAX and mGFP-LactC2 were treated with 2.6 nM oligomycin A for 48 h and then fixed and imaged using a confocal microscope. K-Ras or LactC2 mislocalization from the PM was quantified using Manders coefficients, as described in the legend to panel A, with the value being shown on each image. (D) K-Ras C-terminal sequence. Amino acids in red are putative phosphorylation sites. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide.