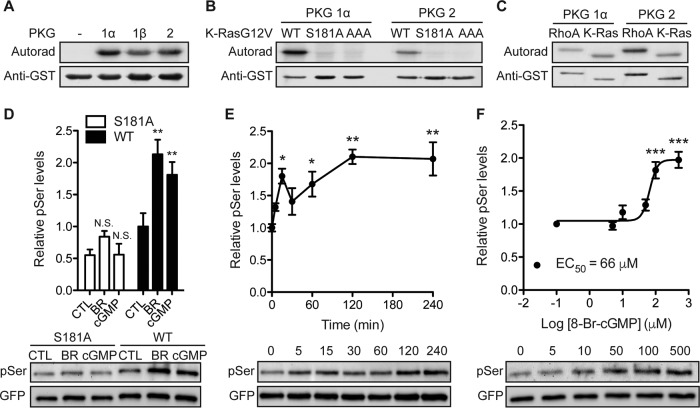
FIG 2.
K-Ras is a substrate for cGMP-activated protein kinases. (A) Recombinant GST–K-Ras was incubated in vitro with purified PKG1α, PKG1β, or PKG2 and [γ-32PO4]ATP. Phosphate incorporation was analyzed by autoradiography (Autorad) (top), and equal loading was determined by anti-GST immunoblotting (bottom). (B and C) In vitro kinase experiments as described in the legend to panel A but including recombinant GST–K-RasG12V with the S181A and AAA (AAA = S171A, S181A, T183A) mutations (B) or recombinant GST-tagged RhoA (C). (D) MDCK cells stably expressing mGFP–K-RasG12V (wild type [WT]) or mGFP–K-RasG12V S181A (S181A) were treated with 1 μM bryostatin-1 (BR) for 5 min or 500 μM 8-Br-cGMP (cGMP) for 15 min. mGFP–K-Ras proteins were immunopurified and immunoblotted with an antiphosphoserine (pSer) antibody after fixation in 4% paraformaldehyde and 0.01% glutaraldehyde. The membranes were stripped and reblotted with an anti-GFP antibody. The graph shows the mean phospho-K-Ras levels ± SEM from three independent experiments, with representative blots being shown. Significant differences between control (CTL; vehicle-treated) and drug-treated cells were assessed using one-way ANOVA tests (**, P < 0.01; N.S., not significant). (E and F) MDCK cells stably expressing mGFP–K-RasG12V were treated with 500 μM 8-Br-cGMP for the indicated times (E) or the indicated concentrations for 15 min (F). Phosphorylated K-Ras was detected as described in the legend to panel D. The graph shows the mean phospho-K-Ras levels ± SEM from three independent experiments, with representative blots being shown. EC50, 50% effective concentration. Significant differences between cGMP-treated and control (PBS-treated) cells were assessed using one-way ANOVA tests (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001).