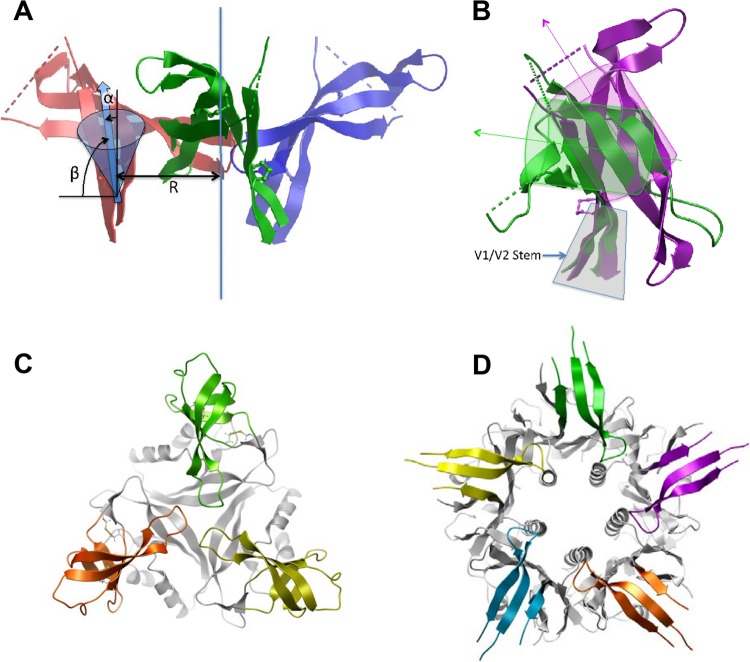
FIG 1.
Designing of V1V2 immunogens. (A) Geometric parameters of the β-hairpin orientation of the V1V2 stem used for scaffold filtering. The 3-fold axis (the vertical blue line) of the trimer, the distance (R) of the V1V2 stem from the axis, and tilting angles (α and β) of the V1V2 stem are illustrated. (B) Differences in stem orientation between V1V2 domain complexes with MAb PG9 (magenta) and MAb 830A (green). Stem strands (highlighted in gray) are superimposed, β-barrels and their axes are indicated schematically as cylinders, and arrows highlight the change in barrel orientation. (C) A top view of V1V2(ZM53)-2J9C. The trimeric scaffold (PDB accession number 2J9C) is shown in gray while the three V1V2s, based on the MAb 830A complexed structure, are shown in green, orange, and gold. (D) A top view of V1V2(ZM109)-TTB. The typhoid toxin subunit B (TTB) pentamer is shown in gray while the V1V2 inserts, shown here as the PG9-bound form, are colored. Note that the V1V2s are placed on top of the pentamer without any hindrance against each other.