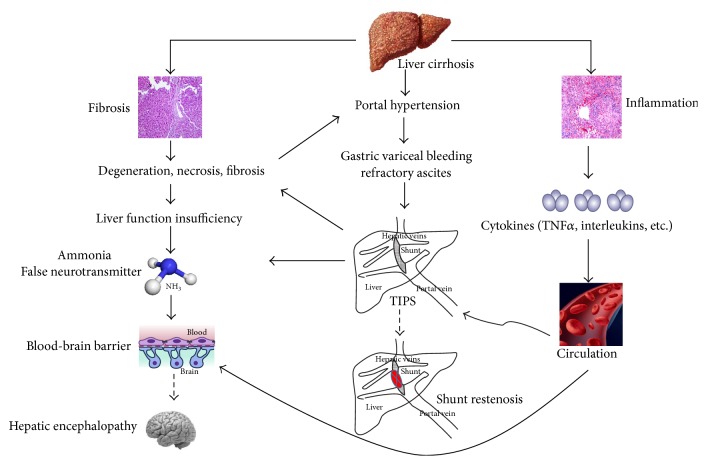
Figure 4.
Hypothesis of shunt restenosis and HE after TIPS. Pathological features of the liver tissues predicted the incidence of shunt restenosis and HE. Elevated levels of cytokines in the circulation induced by inflammation play a critical role in restenosis of the stent, which may serve as the target for treatment. Increased blood ammonia and false neurotransmitter result in liver dysfunction induced by fibrosis, which is aggregated by TIPS. In addition, the release of cytokines induced by inflammation can influence the permeability of the blood-brain barrier (BBB), making it easier for the blood ammonia and false neurotransmitter to cross the BBB, leading to the neurodysfunction, and finally promoting the development of HE.