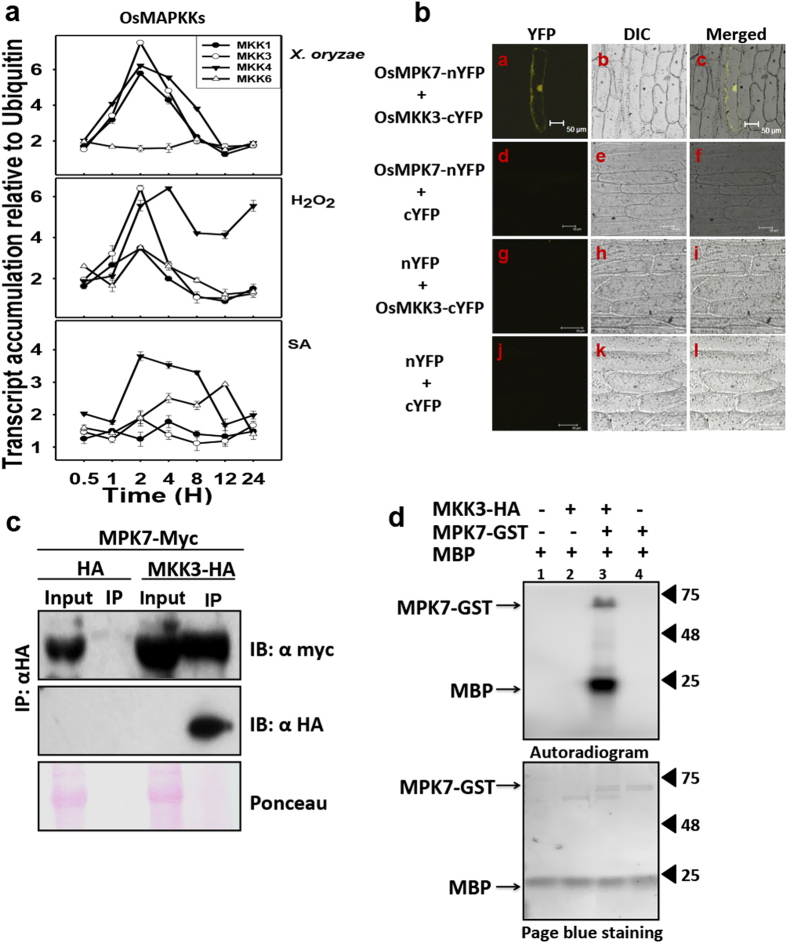
Figure 3. OsMKK3 interacts and activates OsMPK7.
(a) Transcript levels of MAPKK genes were examined in 15 days old rice seedlings in response to X. oryzae, H2O2 and Salicylic acid (SA) treatment. Ubiquitin and actin gene was considered as internal control. The experiments were repeated three times with three technical replicates. (b) Bimolecular fluorescence assay (BiFc) performed using OsMPK7-eYFPN173 and OsMKK3-eYFPC155 fusion protein reveals interaction between OsMPK7 and OsMKK3. YFP fluorescence was observed in onion epidermal cells expressing both OsMKK3 and OsMPK7 fusion proteins as seen in (a) Epifluorescence, (b) bright field and (c) merged images of onion epidermal cells. No YFP fluorescence is observed in negative controls (d,g and j). Scale bar: 50 μm. (c) Immunodetection of complex formation of OsMPK7-Myc and OsMKK3-HA in planta using Co- immunoprecipitaion assay (CoIP). OsMPK7-Myc was co-immunoprecipitated with OsMKK3-HA using anti-HA antibody from plant protein extracts of tobacco leaves transiently expressing both OsMPK7-Myc and OsMKK3-HA. Immunoblotting was carried out with anti-Myc antibody. No band corresponding OsMPK7-Myc is seen in control sample. The lower panel shows the presence of OsMKK3-HA. (d) In vitro kinase assay showing phosphorylation of OsMPK7 by its upstream kinase, OsMKK3. OsMKK3-HA protein was immunoprecipitated from plant protein extract of tobacco leaves transiently expressing OsMKK3-HA and phosphorylated OsMPK7-GST, which in-turn phosphorylated MBP. Phosphorylation signal of OsMPK7 and MBP was detected by autoradiography.