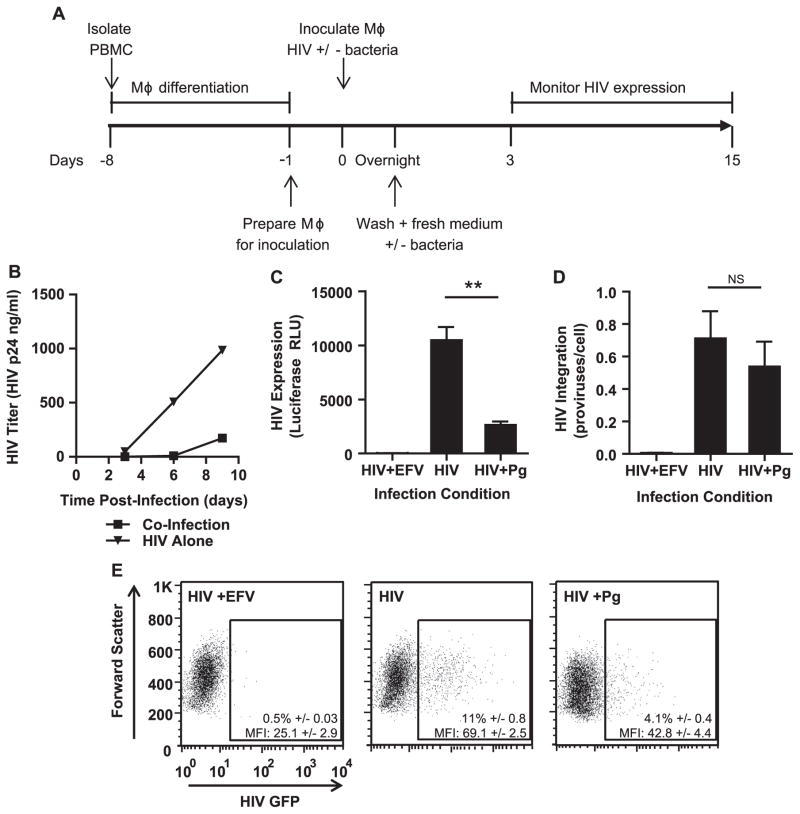
Fig. 2.
The presence of P. gingivalis at the time of infection represses HIV replication in MDMs. (A) General experimental outline to test the effect of heat-killed P. gingivalis on HIV replication in MDMs. (B) MDMs were infected with HIV-WT/BaL with or without exposure to P. gingivalis at an MOI of 10. HIV spread was monitored by HIV-p24 ELISA. Data is representative of 3 independent experiments. To test HIV expression in the context of single round infection, MDMs were infected with HIV-NL4-3ΔEnv-Luc(VSV-G) with or without P. gingivalis (MOI 30) and monitored HIV infection by (C) luciferase expression (D) and Alu-PCR for HIV integration at 3 days post-infection. Cultures treated with 1 μM efavirenz (EFV) served as a negative control. Error bars represent the standard deviation of triplicate measurements. Both graphs were generated from the same experiment and are representative of 3 individual experiments. Asterisks and NS represent p<0.01 and p>0.05 respectively as assessed by Student’s T test. (E) MDMs were infected with HIV-NL4-3ΔEnv-GFP(VSV-G) and monitored GFP expression 3 days post-infection by flow cytometry. Percentages are displayed±the standard deviation of triplicate infections of cells from the same donor. The geometric mean intensity of GFP (MFI) is displayed±the standard deviation of triplicate inoculations of cells from the same donor. The experiment is representative of 3 individual experiments.