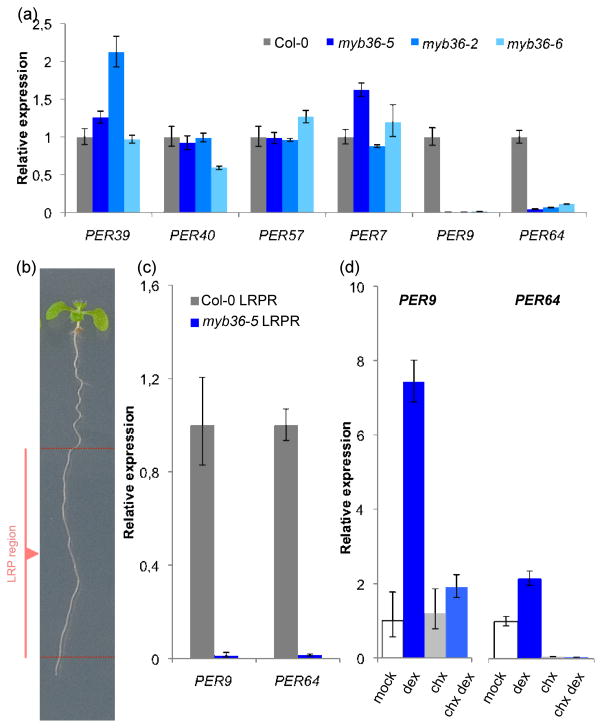
Fig. 3.
Role of Arabidopsis thaliana MYB36 in lateral root primordia (LRP) development through various PER genes. (a) Relative expression of the indicated PER genes in roots of Col-0 and myb36 mutant plants. The only cases where differences were statistically significant and consistent in all mutants analyzed were PER9 and PER64 (P ≤ 0.01). (b) Representative image of the root highlighting the lateral root primordia region (LRPR) of the root. The LRPR of the root comprises the stages of LRP development where MYB36 is expressed (before LR emergence). (c) Abundance of PER9 and PER64 transcript levels in Col-0 and myb36-5 LRPR. Differences were statistically significant (P ≤ 0.01). (d) PER9 and PER64 mRNA levels in pMYB36::MYB36:GR in myb36-5 seedlings treated with dexamethasone (dex) in the absence or presence of cycloheximide (chx). Error bars indicate ± SD.