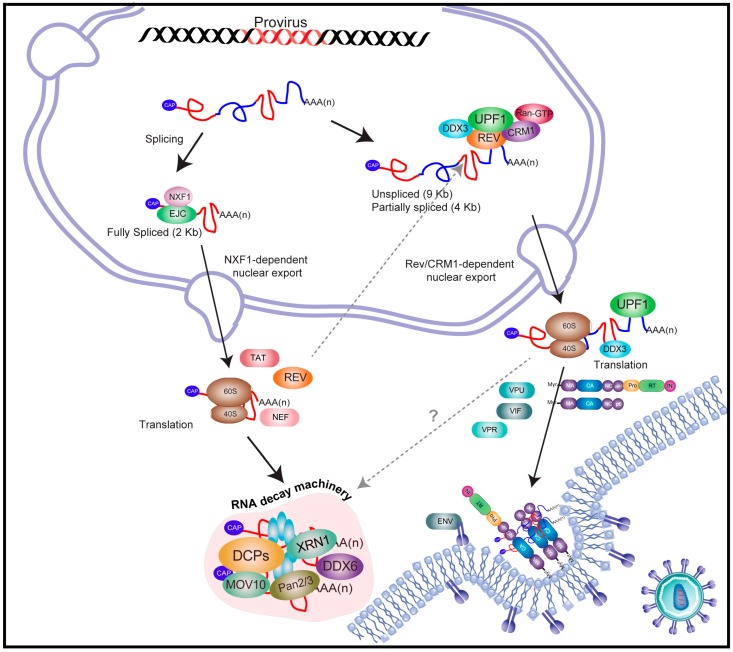
Figure 1.
Post-transcriptional control of gene expression in HIV-1. Upon RNA polymerase II-driven transcription, the capped and polyadenylated 9 kb full-length mRNA undergoes alternative splicing in order to generate the 2 kb fully spliced and the 4 kb partially spliced (omitted for simplicity) transcripts. Fully spliced transcripts follow the canonical pathway for mRNA metabolism, in which nuclear export and translation are ensured by the splicing-dependent recruitment of nuclear factors such as the exon junction complex (EJC) and the mRNA nuclear export factor NXF1. Once in the cytoplasm, fully spliced mRNA recruits the host translational machinery in order to synthesize viral proteins TAT, REV, and NEF and upon several rounds of translation they are degraded by the host RNA decay machinery. The viral protein REV enters the nucleus, allowing the accumulation of the 9 kb unspliced mRNA and its subsequent nuclear export through the chromosomal maintenance 1 (CRM1)-dependent pathway. This alternative nuclear export pathway allows the unspliced mRNA to evade surveillance and quality control mechanisms associated with the canonical nuclear export pathway. During its journey to the cytoplasm, the unspliced mRNA recruits several host proteins such as up-frameshift suppressor 1 homolog (UPF1) and the DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box 3- (DDX3) RNA helicase that will ensure an efficient association with the host translational machinery in order to synthesize the major structural proteins GAG and GAG–POL. In contrast to fully spliced transcripts, the unspliced mRNA does not undergo mRNA turnover as it is used as the viral genome incorporated into viral particles. CA, capsid protein; DCP, decapping enzyme; IN, integrase; MA, matrix protein; MOV10; Moloney leukemia virus 10; Myr, N-terminally myristoylated; NC, nucleocapsid protein; Pan2/3, PAB-dependent poly(A)-specific ribonuclease; p6, p6 protein; Ran-GTP, ras-related nuclear protein GTP; RT, reverse transcriptase; XRN1, 5'-3' Exoribonuclease 1.