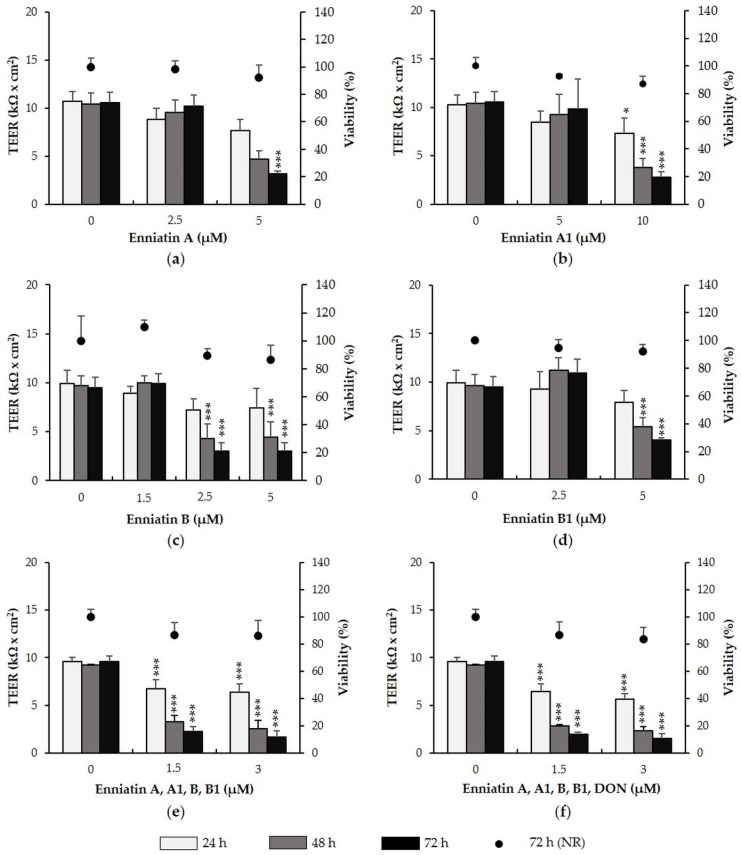
Figure 1.
Effect of enniatin A, A1, B and B1 as well as combinations of enniatins (+/− deoxynivalenol, DON) on transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) and viability of differentiated intestinal porcine epithelial cells (IPEC-J2). IPEC-J2 were treated with (a) enniatin A (2.5 and 5 µM); (b) A1 (5 and 10 µM); (c) B (1.5, 2.5 and 5 µM); or (d) B1 (2.5 and 5 µM); as well as (e) a combination of all enniatins (each toxin: 1.5 or 3 µM); and (f) a combination of all enniatins with DON (each toxin: 1.5 or 3 µM). TEER was measured after 24, 48 and 72 h. After the final TEER measurement, viability was determined via the neutral red (NR) assay. Asterisks indicate significant differences compared to control of the respective time point (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001). Data represent mean ± SD, n = 3.