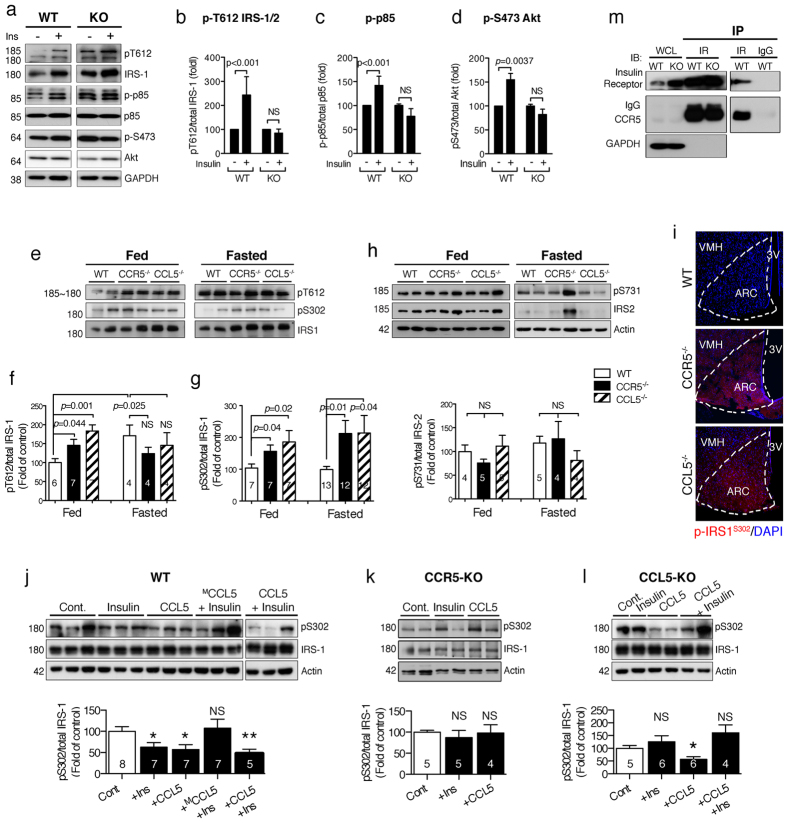
Figure 2. CCR5 association with the insulin receptor participates in hypothalamic insulin signal activation.
(a–d) The hypothalamus tissues from WT and CCR5−/− mice were stimulated with insulin (10 nM) ex vivo. (a) The immunoblot of the insulin signaling molecules as IRS-1, PI3K–p85 and Akt in hypothalamus were activated by insulin in WT but not in CCR5−/− (KO) mice. The quantification results are in (b) for phosphor-IRS-1T612, (c) for phosphor-P85, and (d) for phosphor-AktS473. The phosphorylation status of insulin substrate–IRS-1 and IRS-2 under feeding and fasting were analyzed. (e–g) The activated form of IRS-1 phospho-Tyr612 and inhibitory form of phospho-Ser302 were increased in both fasted and non-fasted CCR5−/− and CCL5−/− mouse hypothalamus. (h) IRS-2 activities in CCR5−/− and CCL5−/− were not different from WT under both non-fasting and fasting conditions. (i) Immunoreactivity of p-IRS-1S302 (red) was detected in the ARC region of CCR5−/− and CCL5−/− mice (Nucleus: blue) (3V: third ventricle, ARC: arcuate nucleus, VMH: ventromedial hypothalamus). (j–l) Hypothalamus tissues isolated from 8 hr fasted mice following stimulation with: (1) PBS for 5 min as control (Cont.), (2) Insulin (Ins, 10 nM) 5 min, (3) CCL5 (10 ng/ml) 5 min, (4) combined insulin and CCL5 (Ins + CCL5) for 5 min, and (5) the CCL5 antagonist–methylated-CCL5 (MCCL5, 10 ng/ml) 10 min pretreatment before insulin (MCCL5 + Ins). The phosph-IRS-1S302 levels under different conditions were analyzed by protein blot. The relative levels of p-IRS-1S302 under various treatments in WT mice (j), CCR5−/− mice (k), and CCL5−/− mice (l) are summarized. (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 compared to control; NS: no significant difference). (m) Hypothalamic tissues from WT and CCR5−/− (KO) were incubated with insulin receptor (IR) antibody or rabbit-IgG (as control) as indicated and immunoprecipitated with protein-A beads. Whole cell lysate (WCL) and co-immunoprecipiated proteins (IP) were probed with insulin receptor (IR), CCR5 and IRS-1. GADPH was used as loading control.