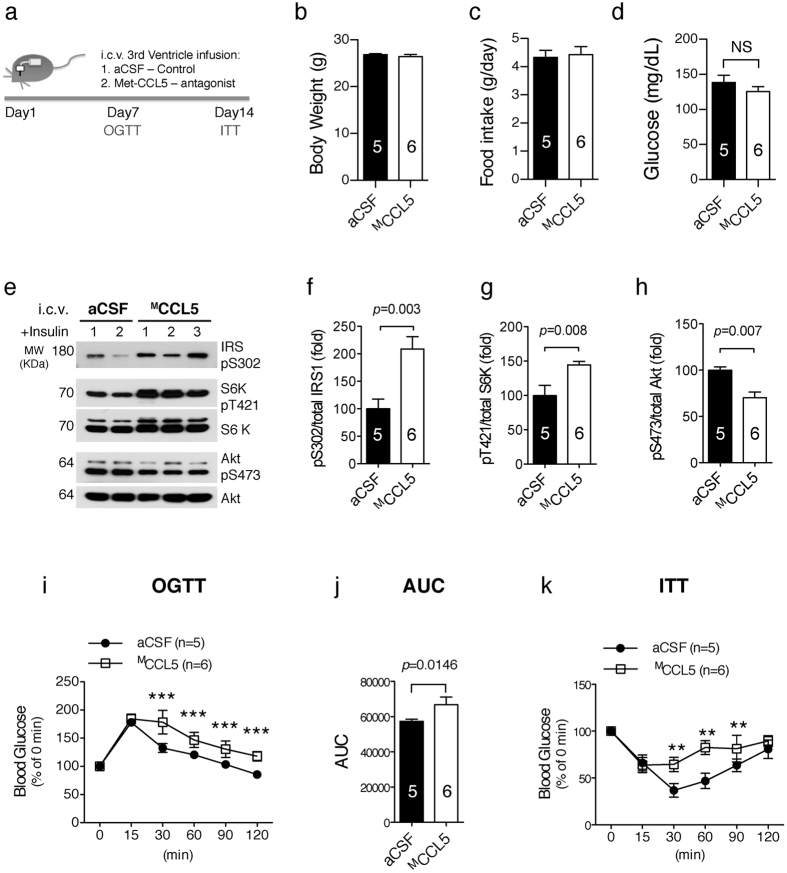
Figure 6. Blocking hypothalamic CCR5 with the antagonist-MCCL5 induced glucose metabolism impairment and insulin resistance peripherally.
(a) Wildtype mice received 3rd ventricle ICV infusion with aCSF as control or a CCL5 antagonist–Met-CCL5 (MCCL5) to block CCR5 over two weeks. The body weight (b), daily food intake (c) and fasting blood glucose (d) in two groups of mice were similar. (e–h) The activation of insulin signaling manifested as phospho-AktS473 was reduced in MCCL5-treated mouse hypothalamus; the inhibitory signals as phosphor-IRS-1S302 and phosphor-S6KT421 were increased in mice receiving the antagonist-MCCL5. OGTT (oral glucose tolerance test) (i), the AUC (area under curve) of OGTT (j), and ITT (insulin tolerance test) (k) were impaired in mice treated with antagonist MCCL5. (n = 5~6 in each groups, ***p = 0.001, **p = 0.0015, by Two-way ANOVA in i, k).