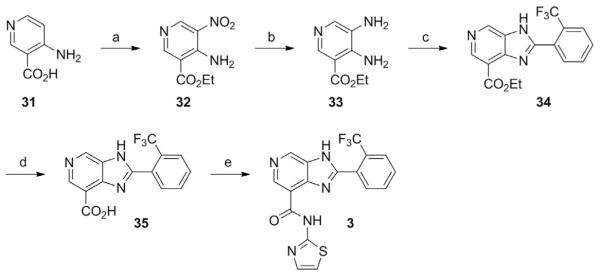
Fig. 3.
Schematic outlining the synthesis of a imidazo[4,5–c]pyridine STAC. Compounds 31–35 represent intermediate products leading toward the production of the STAC N–(thiazol–2–yl)–2–(2–trifluoromethyl–phenyl)–3H–imidazo[4,5–c]pyridine–7–carboxamide (3). Special reagents and conditions noted: (a) KNO3, H2SO4, 0–75°C, then add EtOH, RT to 60°C (35%); (b) H2, 10% Pd/C, MeOH (80%); (c) 3–trifluoromethylbenzaldehyde, Na2S2O5, DMF, 120°C (70%); (d) 10% aq. NaOH, EtOH, reflux, then 5 N HCl (85%); (e) thiazol–2–amine, HATU, (i–Pr)2NEt, DMF, RT (12%). Adapted from Hubbard, B. P., Gomes, A. P., Dai, H., Li, J., Case, A. W., Considine, T., …, Sinclair, D. A. (2013). Evidence for a common mechanism of SIRT1 regulation by allosteric activators. Science, 339(6124), 1216–1219.