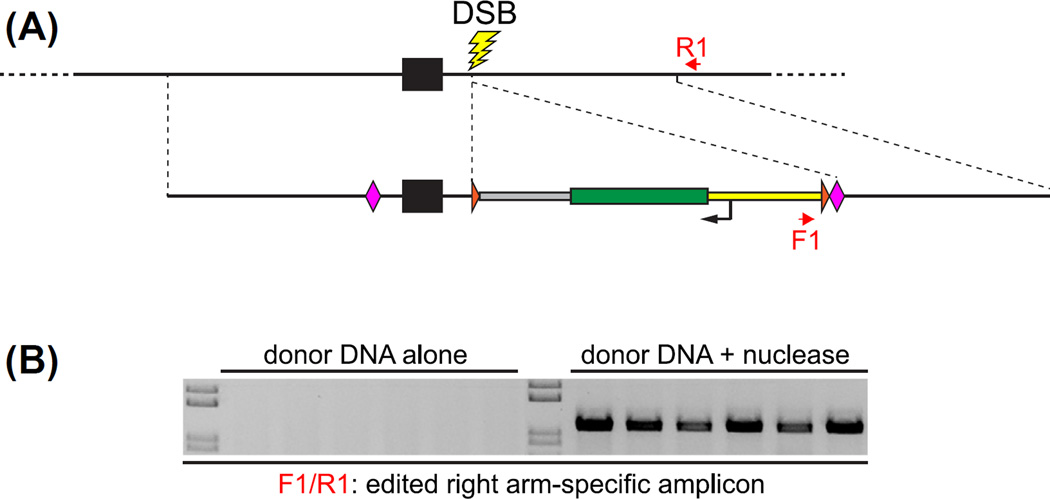
FIGURE 3. PCR-based screening to identify edited alleles in F0 embryos.
(A) Schematic representation (as in Fig. 2) of a genome-editing event in which HR with the dsDNA donor molecule introduces a pair of loxP recombination sites flanking an exon as well as the α-crystallin::GFP reporter gene. To detect the presence of correctly edited alleles in F0 embryos that had been injected with nuclease and donor molecules, genomic DNA is isolated from individual 1 dpf F0 embryos, and PCR analysis is performed using one primer (F1) specific to novel donor sequences and a second primer (R1) specific to endogenous host sequences distal to the homology region. (B) HR is dependent on nuclease activity. When donor DNA is injected without nuclease, edited alleles are not detected in F0 embryos. However, under typical efficient editing conditions, following injection of donor DNA with nuclease, every F0 embryo harbors precisely edited alleles.