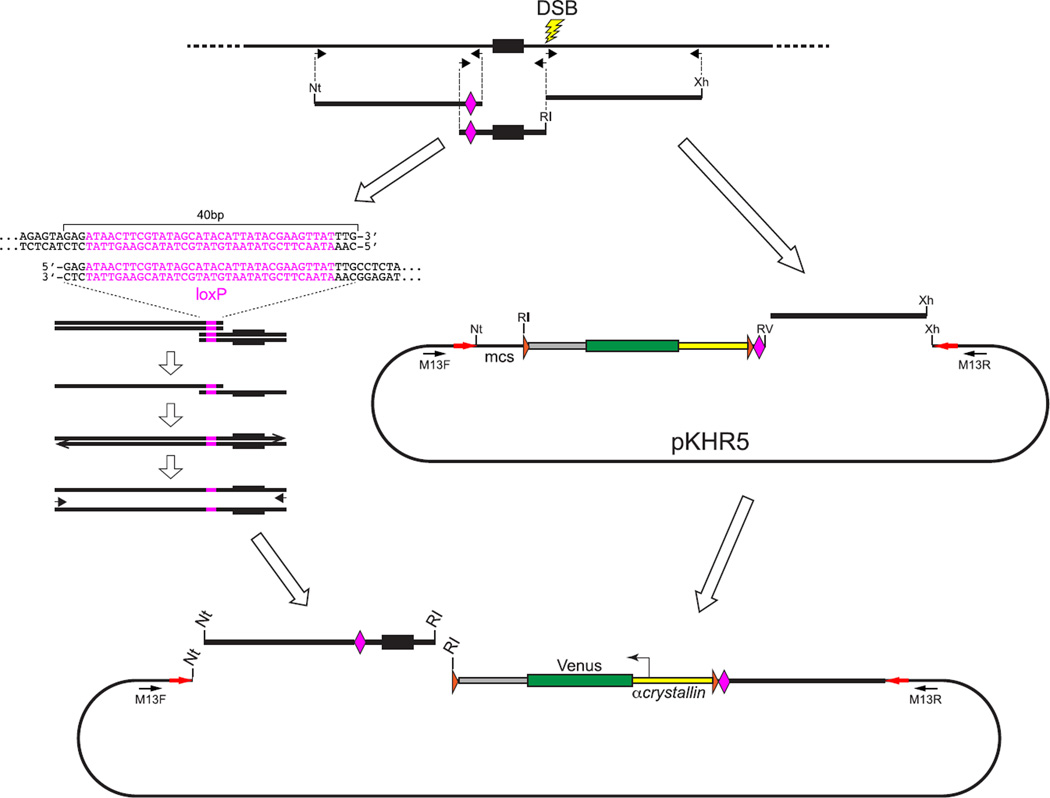
FIGURE 8. Preparation of a donor plasmid to create a loxP-flanked conditional allele marked by a linked reporter gene.
A donor plasmid to create a conditional allele in which loxP sites flank an exon can be constructed using the pKHR5 or pKHR8 vectors (Fig. 6). These vectors provide the CV reporter gene cassette, which consists of the α-crystallin::Venus reporter gene flanked by FRT sites (orange arrowheads) with a single loxP site (pink diamond) located at the border between the reporter and the right homology arm. The right homology arm, consisting of about 1-kbp sequence extending 3′ from the lesion site, is amplified with primers to produce a blunt phosphorylated 5′ end and a 3′ end with an XhoI (Xh) site. The right arm is then cloned into an EcoRV + XhoI-digested vector. As illustrated, the vector-provided loxP site will be inserted into intron sequences downstream (3′) of the targeted exon, and so a second loxP site needs to be introduced into an extended left homology arm, 5′ to the exon. The left arm containing the loxP site is prepared by overlapping PCR amplification to create a fused template from two fragments initially generated from the targeted locus. One fragment contains the exon, extending from the DSB lesion site to the intended position of the second loxP site. Primers used to generate this fragment introduce novel end sequences, an EcoRI (RI) recognition sequence at the lesion site and a 40-bp sequence that includes the loxP site at the end terminating 5′ of the exon. The second fragment extends about 1 kbp further upstream from the position of the loxP site. Primers used to generate this amplicon produce a fragment bordered 5′ by a NotI (Nt) site and 3′ by the 40-bp sequence that includes the loxP site. Overlapping PCR is used to generate a single extended left-arm fragment that is bordered by NotI and EcoRI sites and extends from the lesion site into the upstream intron. The left arm is cloned into a NotI + EcoRI digested vector that already contains the right arm homology. (See color plate)