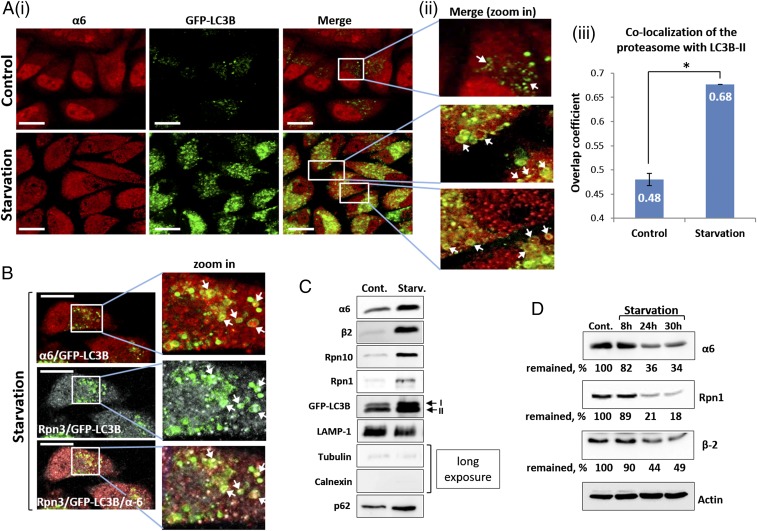
Fig. 1.
Autophagic uptake of the proteasome and its subsequent degradation are induced by amino acid starvation. (A) (i) HeLa cells stably expressing GFP-LC3B were incubated for 4 h in the presence of complete (Upper) or amino acid-depleted medium (Lower). Fixed cells were stained with anti-α6 antibody (red). (Scale bars: 20 μm.) (ii) Highly magnified fields. White arrows point to proteasome-containing autophagosomes. (iii) Manders overlap coefficients of LC3B-II (GFP) and α6 (red) colocalization were calculated. *P < 0.0000012. (B) Immunofluorescent staining of GFP-LC3B–transfected HeLa cells with anti-α6 (red; Upper) and Rpn3 (gray; Middle) antibodies following 4 h of amino acid starvation. (Scale bars: 20 μm.) White arrows point to the 20S CP (merge, zoom in; Upper) and 19S RP (merge, zoom in; Middle) within autophagosomal vesicles. (Lower) Merged image of α6, Rpn3, and LC3B-II. (C) Autophagosome-lysosome vesicles were purified from control (Cont.) and 4 h starved cells (Starv.). Isolated vesicles were lysed, resolved via SDS/PAGE, and subjected to immunoblotting with anti-α6 and anti-β2 (20S CP); with anti-Rpn10 and anti-Rpn1 (19S RP); and with anti-LAMP1 (lysosome), anti-tubulin, anti-calnexin and anti-p62 (autophagic machinery). (D) GFP-LC3B–expressing HeLa cells were left untreated (Cont.) or starved for the indicated times. Cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting after electrophoresis with anti-α6, anti-Rpn1, anti-β2, and anti-actin.