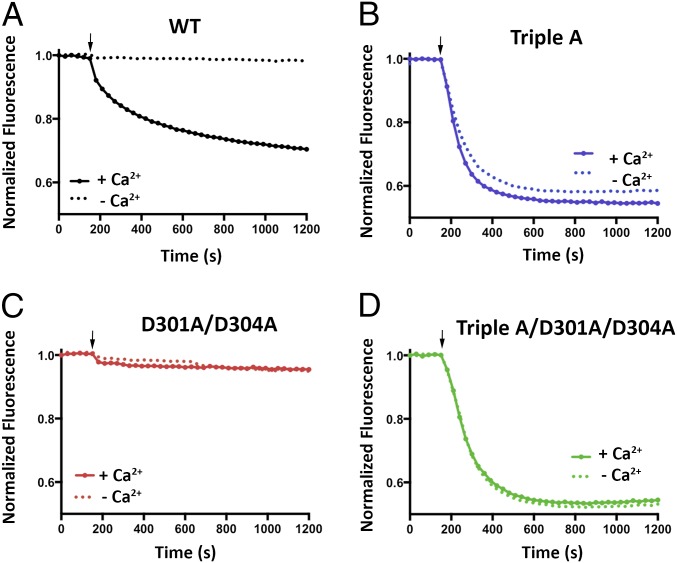
Fig. 4.
Cl− flux analysis of BEST1TripleA and Ca2+ clasp mutants. (A–D) For each assay, proteoliposomes were diluted 100-fold into flux assay buffer containing either 1 mM EGTA (- Ca2+) or 1 mM EGTA-CaSO4 (+ Ca2+, [Ca2+]free ∼ 2 μM). The arrow indicates when the assay was initiated by the addition of the proton ionophore CCCP. (A) Cl− flux of BEST1WT is Ca2+ dependent. (B) Cl− flux through BEST1TripleA is observed regardless of the presence or absence of Ca2+. (C) Mutation of aspartate amino acids that coordinate Ca2+ in the Ca2+ clasp to alanine (D301A/D304A) abolishes Cl− flux and makes the channel unresponsive to 2 µM Ca2+. (D) Combining the D301A/D304A and the BEST1TripleA mutations produces a constitutively active channel that is not responsive to the Ca2+ concentration. The increased flux observed for BEST1TripleA relative to BEST1WT is partially due to the nature of the assay, where Ca2+ is only added to the outside of the vesicles. For BEST1WT, only those channels with their Ca2+ sensors facing outside are reactivated, whereas Cl− flux through BEST1TripleA channels in both orientation is detected because these channels conduct Cl− in a Ca2+-independent manner.