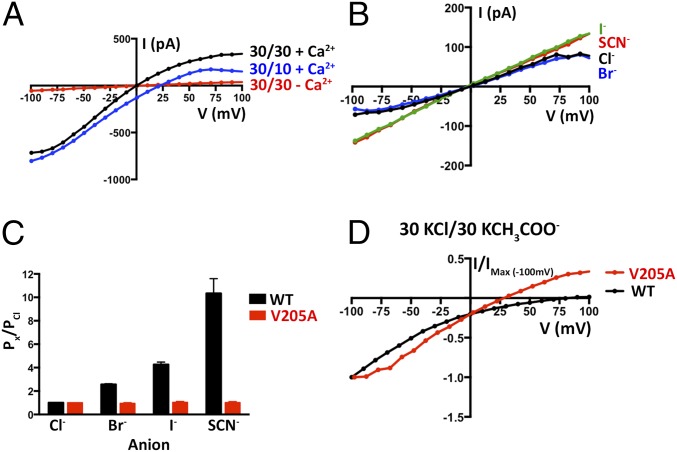
Fig. 6.
Function of the aperture. (A) Observed BEST1V205A currents are Cl− selective and Ca2+ dependent. Example I–V relationships are shown for voltages stepped from −100 to +100 mV for BEST1V205A for the indicated standard conditions [cis/trans KCl concentrations in millimolar, and 300 nM Ca2+ (+ Ca2+) or 10 mM EGTA (-Ca2+)]. (B) The V205A mutation abolishes the lyotropic permeability sequence of BEST1. I–V traces are shown for procedures equivalent to Fig. 1G. After first recording using symmetric 30 mM KCl (black I–V trace), the solution on the trans side was replaced (by perfusion) with solutions containing 30 mM KBr, KI, or KSCN. (C) Comparison of PX/PCl for BEST1WT and BEST1V205A. Using data from experiments carried out as in B, permeability ratios were determined by solving the Goldman–Hodgkin–Katz equation (SI Extended Data Analysis). Three separate experiments were used to compute the SEM. (D) BEST1V205A shows increased permeability to acetate (CH3COO−) compared with BEST1WT. Representative I–V relationships using solutions containing 30 mM KCl on the cis side and 30 mM KCH3COO− on the trans side are shown for BEST1WT and the V205A mutant. For the comparison, the currents were normalized to the values recorded at −100 mV (Imax = −62 and −105 pA for BEST1WT and the V205A mutant, respectively, in this experiment).