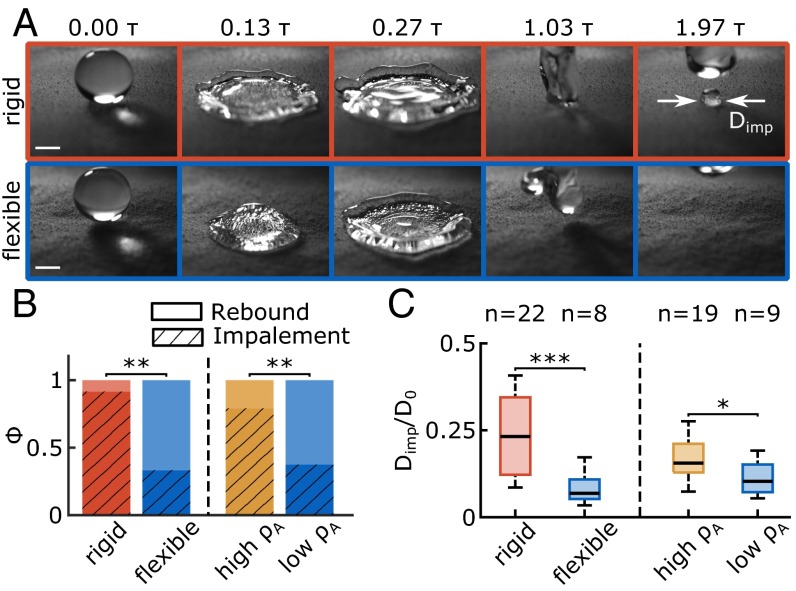
Fig. 1.
Comparison of impalement resistance between rigid and flexible/high areal density substrates. (A) Image sequence showing a droplet ( 2.35 mm, 50) impacting on rigid (Upper) and flexible (Lower) superhydrophobic surfaces (nC1 coating). (Scale bar, 1 mm.) (B) Probability of impalement (, hatched) and full rebound (, filled) for droplet impacts on the rigid and flexible substrates (left, 2.35 mm, 50, 24) and flexible substrates with low and high areal density (right, 2.35 mm, 69, 24). (C) Relative diameter of impalement zone () in the case where impalement did occur during the droplet impact event. Data correspond to the impalement events depicted on B. Box spans from the first to third quartile with Tukey style whiskers, and bold lines indicate population medians. Sample size () is indicated above each box. Significant differences are indicated by asterisks (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001).