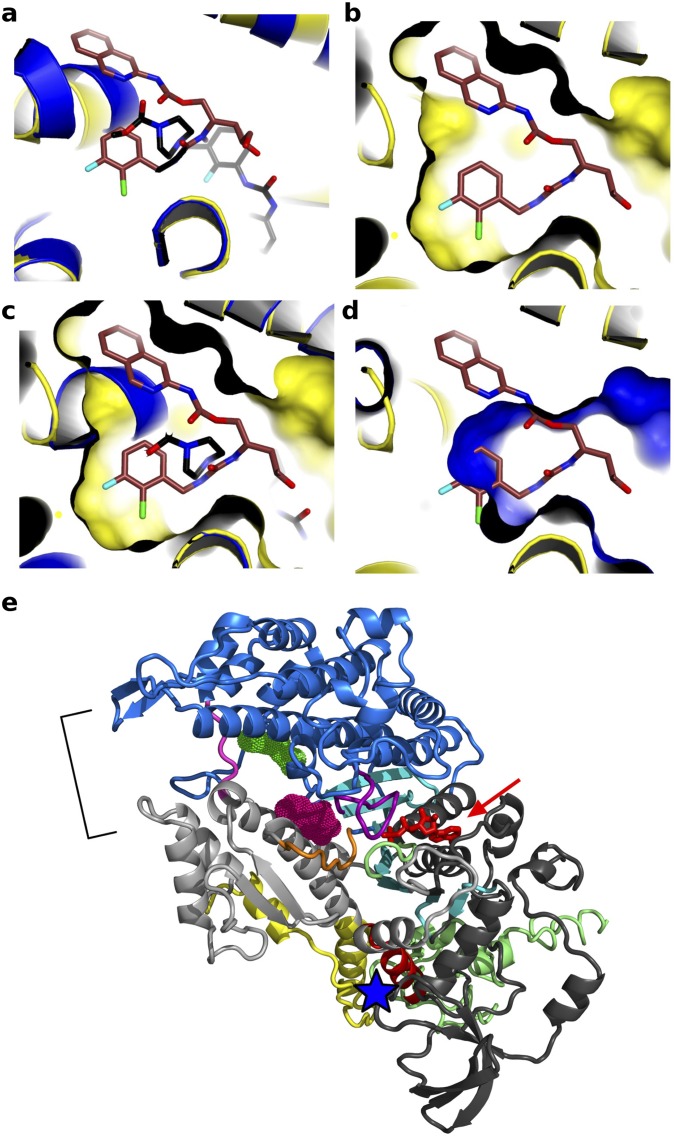
Fig. S4.
Modulators of myosin activity differently influence the recovery stroke and its ability to produce force. Shown is a representation of the CK-571 (brown) and omecamtiv mecarbil (PDB ID code 4PA0, black) binding pockets. The binding site for CK-571 (orange) is distinct from that of myosin activator omecamtiv mecarbil (blue). Note that there is poor superimposition between the structural elements that surround the ligand binding pockets (A) and none of the rings of CK-571 fit in the pocket in which omecamtiv mecarbil binds (B–D). Note in particular how the binding surface of CK-571 (B) differs from that of omecamtiv mecarbil (D). (E) Representation of the Dictyostelium discoideum myosin II structure (PDB ID codes 2JHR and 1YV3) in a PPS state showing that blebbistatin (pink) and pentabromopseudilin (green) occupies surface pockets of the PPS state that are close to the ATP (red arrow) or the actin binding site (bracket), respectively. These sites are distant from the CK-571 site (blue star). Note that no pocket is available for CK-571 binding in the PPS state.