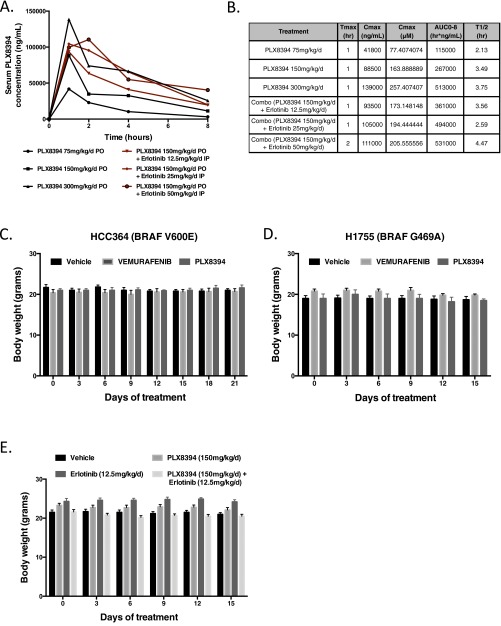
Fig. S2.
Pharmacokinetics and toxicity of PLX8394 in vivo. (A) PLX8394 was given orally at 75 mg⋅kg−1⋅d−1, 150 mg⋅kg−1⋅d−1, or 300 mg⋅kg−1⋅d−1, and serum concentration (ng/mL) was measured at 0, 1, 2, 4, and 8 h after treatment (black lines). PLX8394 150 mg⋅kg−1⋅d−1 was given orally with erlotinib 12.5 mg⋅kg−1⋅d−1, 25 mg⋅kg−1⋅d−1, or 50 mg⋅kg−1⋅d−1, and serum concentration (ng/mL) was measured at 0, 1, 2, 4, and 8 h after treatment (red lines). (B) In vivo pharmacokinetics of PLX8394 monotherapy or in combination with erlonitib. AUC0-8, area under the curve 0–8 h; Cmax (μM), maximum serum concentration in μM; Cmax (ng/mL), maximum serum concentration in ng/mL; T1/2, half-life; Tmax, time to maximum concentration. (C and D) Weights derived from mice bearing either orthotopically (HCC364 cells) or s.c. (H1755 cells) implanted tumor cells and treated with either vehicle, vemurafenib, or PLX8394 for 21 (orthotopic) or 15 (s.c.) days, respectively. (E) Weights derived from mice treated with vehicle, erlotinib 12.5 mg⋅kg−1⋅d−1, PLX8394 150 mg⋅kg−1⋅d−1, or combination PLX8394 150 mg⋅kg−1⋅d−1 and erlotinib 12.5 mg⋅kg−1⋅d−1 for 14 d.