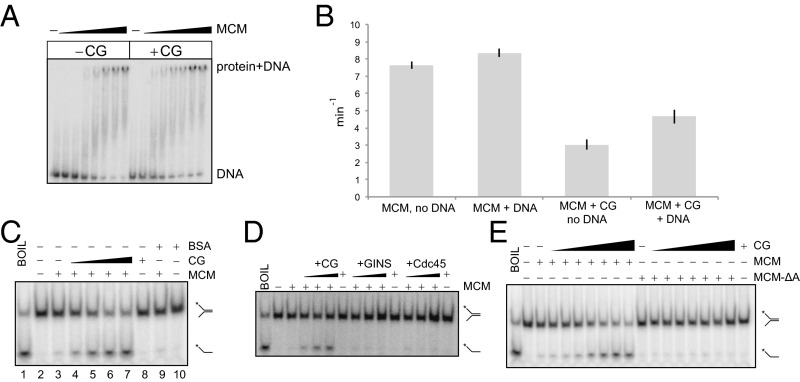
Fig. 5.
Effect of CG on the biochemical properties of MCM. (A) EMSA analysis of MCM binding to 2 nM Y-shaped oligonucleotide DNA in the presence and absence of 500 nM CG. MCM concentrations were 5, 7.5, 10, 12.5, 15, 17.5, and 20 nM hexamer. (B) ATPase measurements of 100 nM MCM (hexamer) supplemented with 1 µM CG or corresponding buffer control. Where added, single-stranded DNA was at 1 µM. (C) DNA helicase assays with MCM and CG complex. DNA substrate was 1 nM. MCM was at 20 nM as hexamer; increasing amounts (125, 250, 500, 1,000 nM) of CG complex and 1 µM BSA as indicated were added. The control lane with CG complex alone had CG at 1 µM. (D) DNA helicase assays for MCM with CG complex, GINS, and Cdc45 separately. MCM was added 20 nM as hexamer; increasing amounts (125, 250, 500 nM) of CG complex, GINS, and Cdc45, as indicated, were added. Reactions with CG, GINS, or Cdc45 contained the indicated protein at 500 nM. (E) DNA helicase assays with MCM, MCM-ΔA, and CG complex. MCM and MCM-ΔA were added to 20 nM as hexamer; increasing amounts (15, 31, 62, 125, 250, 500, 1,000 nM) of CG complex, as indicated, were added. CG alone in a reaction without MCM or MCM-ΔA was at 1 µM.