Fig 1.
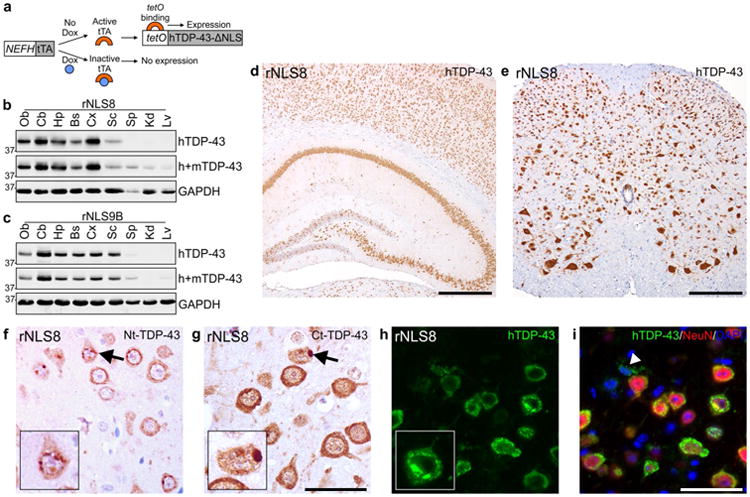
Expression of hTDP-43ΔNLS in brain and spinal cord of rNLS8 and rNLS9B mice. a Schematic for Dox-regulatable expression of hTDP-43ΔNLS in bigenic mice under the control of the NEFH promoter. Expression of hTDP-43 and total (h+m) TDP-43 protein in olfactory bulb (Ob), cerebellum (Cb), hippocampus (Hp), brainstem and remainder of the brain (Bs), cortex (Cx), spinal cord (Sc), spleen (Sp), kidney (Kd) and liver (Lv) of b rNLS8 and c rNLS9B mice at 4 weeks off Dox. Approximate molecular weight markers in kDa are shown on the left and GAPDH is a loading control. Representative immunoblots of n = 3. Representative images at 1 week off Dox show widespread expression of hTDP-43ΔNLS in d Hp, Cx, and e Sc of rNLS8 mice. IHC in rNLS8 motor cortex showing cytoplasmic TDP-43 inclusions (arrows) detected with both f an N-terminal (Nt)-TDP-43 antibody, and g a C-terminal (Ct)-TDP-43 antibody, at 2 weeks off Dox. h, i There is widespread hTDP-43 expression (green) in NeuN+ neurons (red), shown at 4 weeks off Dox. Arrowhead in i indicates rare non-neuronal hTDP-43-positive glial cell, and nuclei are shown by DAPI (blue). Scale bars d 500 μm, e 200 μm, f, g 50 μm, h, i 50 μm
