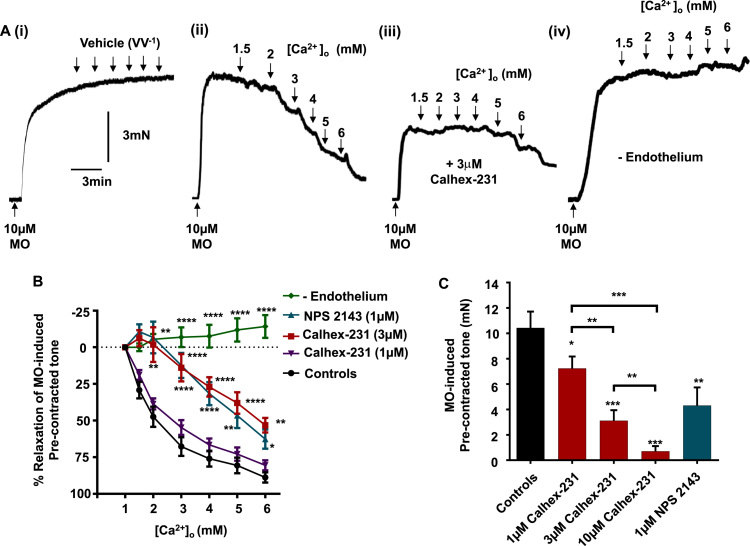
Fig. 1.
Effect of CaSR stimulation and calcilytics on pre-contracted rabbit mesenteric arteries. (A) Representative traces showing the effect of increasing [Ca2+]o on pre-contracted arteries induced by 10 µm methoxamine (MO). Record (i) shows that MO induces a stable vasoconstriction in the presence of 1 mM [Ca2+]o, and the effect of adding increasing volumes of distilled H2O to the myograph bath. Record (ii) shows the effect of increasing [Ca2+]o from 1 mM to 6 mM. Record (iii) shows that the presence of Calhex-231, inhibits both [Ca2+]o-induced vasorelaxations and amplitude of methoxamine-induced vasoconstriction. Record (iv) demonstrates the effect of removing the endothelium on Ca2+]o-induced vasorelaxations. (B) Mean data showing that [Ca2+]o-induced vasorelaxations are attenuated in the presence of 3 µm Calhex-231, 1 µm NPS 2143, and removal of the endothelium. 1 µm Calhex-231 however is without effect. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001, 2-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test. (C) Mean data showing the effect of 1, 3 and 10 µm Calhex-231 or 1 µm NPS 2143 on mean amplitude of the methoxamine-induced pre-contracted arteries. Each point is from n=4 animals, with at least n=3 vessel segments per animal. Student's t-test, **P<0.01.