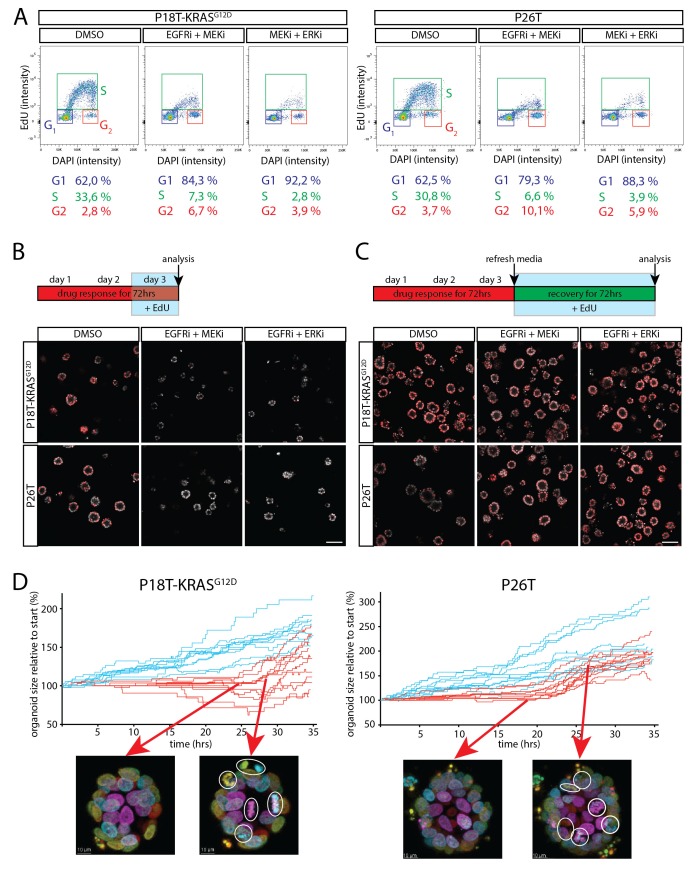
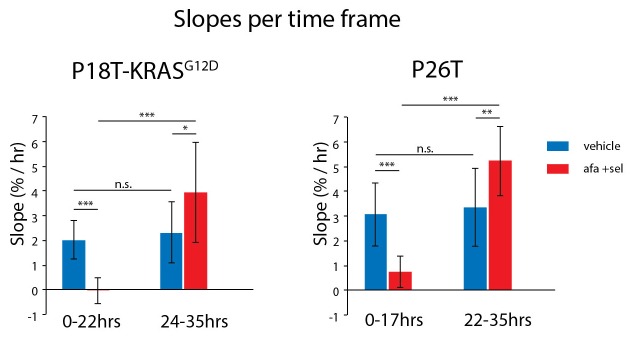
Figure 8. Cell cycle arrest upon dual inhibition of EGFR-MEK-ERK pathway.
(A) Representative cell cycle analysis of P18T-KRASG12D and P26T by flow cytometry (n = 2). DNA was stained with DAPI and DNA-synthesis was detected using a 3 hr EdU pulse to clearly discriminate between G1, S and G2 stages of the cell cycle. Dual inhibition of the EGFR-MEK-ERK pathway significantly changes the distribution of cells between stages of the cell cycle (Chi2: all p values<0,0001) with a predominant increase in G1 at the expense of cells in S-phase. EGFRi + MEKi = afatinib + selumetinib. MEKi + ERKi = selumetinib + SCH772984. (B) Almost no incorporation of EdU (red) is detected during the last 24 hr of drug treatment using dual inhibition of the EGFR-MEK-ERK signaling pathway, indicative of halted proliferative activity. Nuclei are counterstained with Hoechst (white). EGFRi + MEKi = afatinib + selumetinib. EGFRi + ERKi = afatinib + SCH772984. Scale bar is 100 µm. (C) Virtually all cancer cells incorporate EdU (red) when provided after release from targeted inhibition of the EGFR-MEK-ERK pathway. Nuclei are counterstained with Hoechst (white). EGFRi + MEKi = afatinib + selumetinib. EGFRi + ERKi = afatinib + SCH772984. Scale bar is 100 µm. (D) Chronological ranking of mitotic and apoptotic events extracted from live-cell imaging data of tumor recovery reconstructs the organoid size evolution over time. In contrast to vehicle treated organoids (blue lines), afatinib + selumetinib treated organoids (red lines) show first mitotic activity again from 20–24 hr onwards after drug withdrawal. Typical snapshots of live-cell imaging data are provided. White circles indicate mitotic events. Arrows indicate the organoid and moment of snapshot.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18489.030