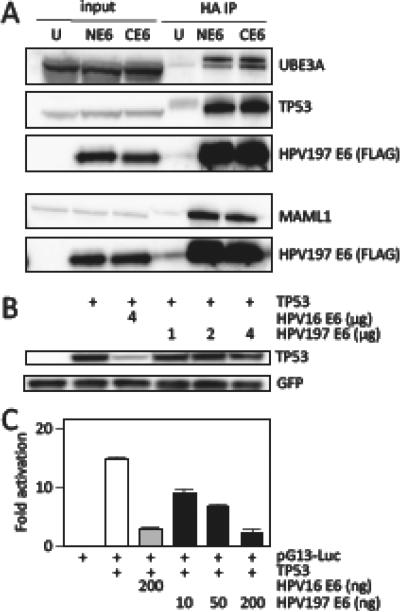
Figure 2.
Binding of HPV197 E6 to the LXXLL domain proteins UBE3A and MAML1 proteins and to TP53. (A) Immunoprecipitation/western blot experiments documenting interaction of ectopically expressed amino (N) and carboxyl (C) terminally HA/FLAG epitope tagged HPV197 E6 proteins with endogenously expressed MAML1, UBE3A and TP53 in HCT116 cells. Input lanes contain 4% of protein extracts used for HA immunoprecipitation (HA IP). HPV197 E6 levels were assessed by immunoblotting with a FLAG antibody. The results of a single IP are shown. UBE3A and TP53 binding was analyzed separately from MAML1 binding. (B) TP53 destabilization assays performed by transient expression of the indicated proteins in Saos-2 osteosarcoma cells. TP53 steady state levels were determined by western blotting. A GFP blot is shown to normalize TP53 levels by transfection efficiency. HPV16 E6 was used as a positive control for TP53 destabilization. (C) TP53 dependent transcriptional reporter assays. The corresponding plasmids were transfected into Saos-2 osteosarcoma cells and firefly luciferase activity was determined. Values were normalized to co-transfected renilla luciferase expression and represent averages and standard deviations from an experiment performed in triplicate. HPV16 E6 was used as a positive control for repression of TP53 transcriptional activity. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments.