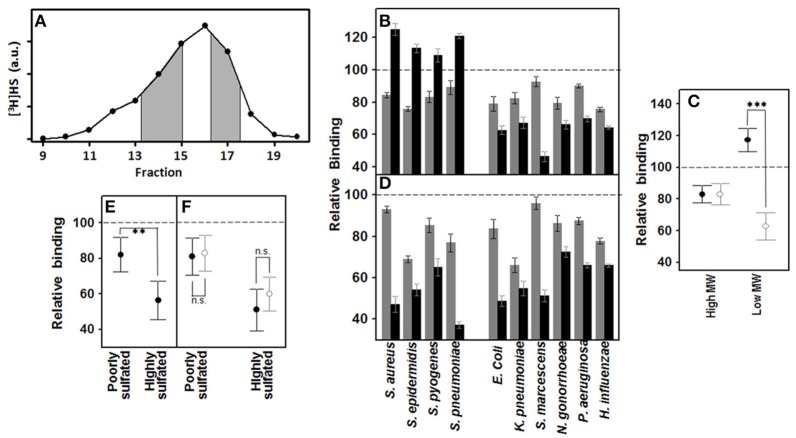
Figure 3.
Effect of the HS chain size and sulfation of domains on pathogen attachment to corneal epithelial cells. (A–C) Effect of high and low MW HS on pathogen attachment to corneal epithelial cells. (A) Size exclusion chromatography of HS; fractions collected, corresponding to areas of both high and low MW, are shaded. (B) Effect on attachment of pathogens to HCE-2 cells: gray bars indicating high MW and black bars, low MW. (C) Adherence differences of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria in the presence of high and low MW HS. (D–F) Effect of highly and poorly sulfated HS domains on pathogen attachment to corneal epithelial cells. (D) Effect on attachment of corneal pathogens: gray bars represent NA-domains and black bars, NS-domains. (E) Comparative effect of NA- and NS-domains on bacterial adherence to corneal cells. (F) Adherence differences of Gram-positive (●) and Gram-negative (○) bacteria in the presence of HS NA- and NS-domains. The spreads represent the standard deviations. Statistically significant differences are denoted by ***, and **, which indicate p < 0.001, and p < 0.01, respectively. n.s. indicates that differences were not significant.