FIGURE 2.
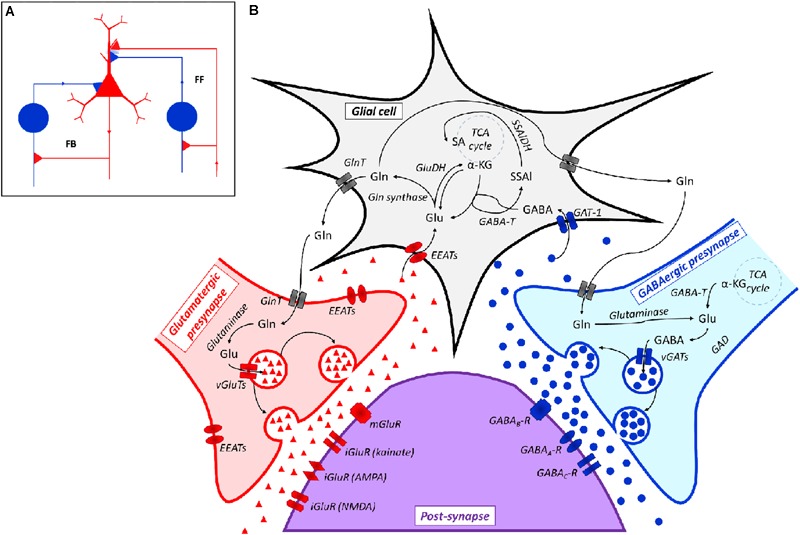
(A) Representation of a Glutamatergic/GABAergic neural network, including an excitatory (Glutamatergic) pyramidal neuron (red), inhibitory (GABAergic) neurons (blue) and the related connections. The inhibitory neuron on the left is integrated into a feedback (FB) circuit, while the inhibitory neuron on the right is integrated into a feed-forward (FF) loop. Inhibitory synapses targeted to the soma or dendrites of the pyramidal cell are surrounded by light blue staining, which indicates a background GABA concentration that contributes to the overall inhibition (adapted from Roth and Draguhn, 2012). (B) Scheme of the Glutamatergic/GABAergic neurotransmission in the CNS. α-KG, α-keto-glutarate; EEATs, excitatory amino acid transporters; GABA, γ-aminobutyric acid; GABAA-R, GABAA receptor; GABAB-R, GABAB receptor; GABAC-R, GABAC receptor; GABA-T, GABA transaminase; GAD, Glu decarboxylase; GAT-1, GABA transporter 1; GlnT, glutamine transporter; Glu, glutamate; iGluR, ionotropic Glu receptor; mGluR, metabotropic Glu receptor; SSAl, succinic semialdehyde; SSAlDH, succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase; TCA cycle, the Krebs cycle; vGAT, vesicular GABA transporter; vGluT, vesicular Glu transporter. Symbols: ●, GABA; ▲, Glu.
