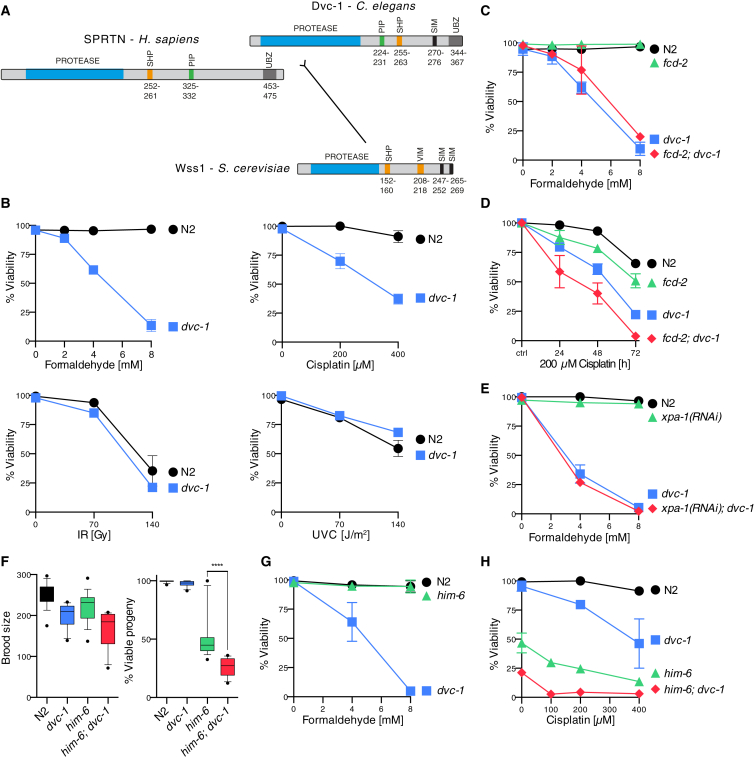
Figure 1.
SPRTN/Dvc-1 Provides Resistance toward DPC-Inducing Agents in Worms and Operates Independently of FANCD2/Fcd-2 and Parallel to BLM/Him-6
(A) Domain structures and evolutionary distances of the protease domain of SPRTN/Wss1 protease family members of humans, worms, and budding yeast. SPRTN/Wss1 proteases bear interaction domains for p97/Cdc48 (SHP-box, VIM), recognition modules for ubiquitin (UBZ) or SUMO (SIM), and in metazoans a PCNA-interaction motif (PIP-box).
(B) C. elegans mutant strains lacking functional SPRTN (dvc-1) are specifically sensitive to the DPC-inducing agents. Formaldehyde sensitivity was determined in synchronized L1 larvae. Cisplatin, UVC light, and IR sensitivities were assessed by measuring embryonic survival of progeny after exposure of adult animals. Error bars indicate SEM of –two to four independent experiments.
(C) FANCD2 is not involved in providing formaldehyde resistance in synchronized L1 larvae. Error bars indicate SEM of two independent experiments.
(D) FANCD2 provides resistance to chronic cisplatin exposure by a mechanism distinct to DPC repair by SPRTN. Viability was assessed by determination of embryonic survival of progeny of young adult animals kept on cisplatin-containing plates (200 μM) for the indicated amount of time. Error bars indicate SEM of two independent experiments.
(E) Loss of XPA does not result in increased formaldehyde sensitivity in synchronized L1 worms. Error bars indicate SEM of two independent experiments.
(F) Loss of SPRTN (dvc-1) results in viability defects in worms lacking the BLM helicase (him-6). Data were obtained from at least 16 animals per indicated genotype. Whiskers indicate tenth to 90th percentiles. Statistical significance was tested using an unpaired t test.
(G) The BLM helicase (Him-6) is not involved in providing formaldehyde resistance in synchronized L1 larvae. Error bars indicate SEM of two independent experiments.
(H) BLM (Him-6) provides resistance to cisplatin exposure by a mechanism parallel to DPC repair by SPRTN. Cisplatin sensitivity was assessed by measuring embryonic survival of progeny after exposure of adult animals. Error bars indicate SEM of two independent experiments.
See also Figure S1.