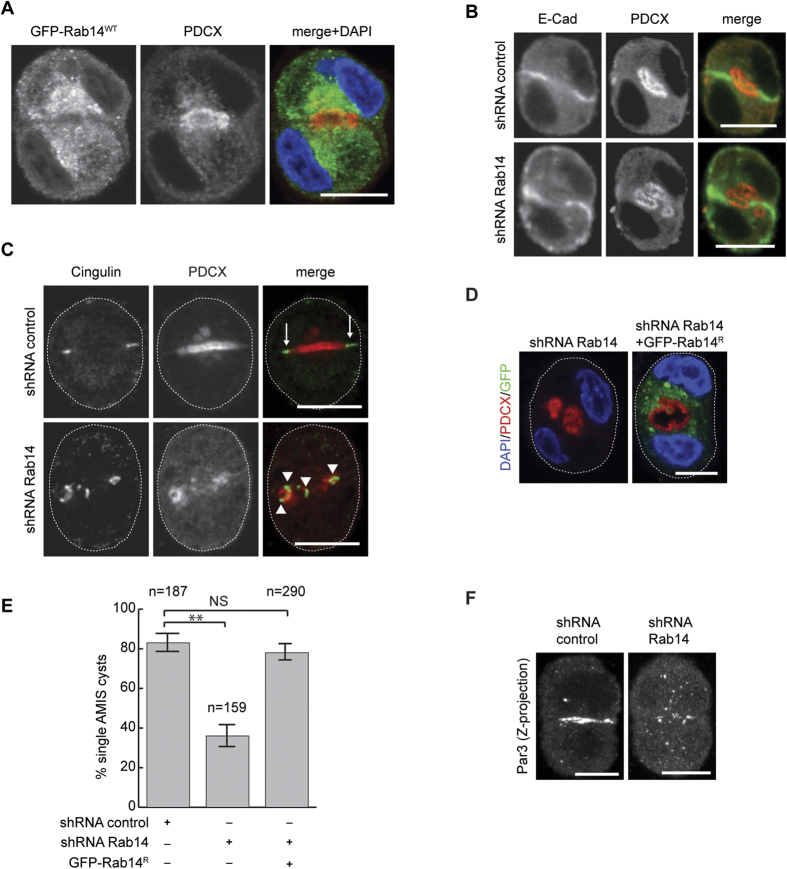
Figure 1. Rab14 is required for initiation of a single apical domain.
(A) MDCK cells expressing GFP-Rab14 were plated in Matrigel and grown for 16 h, fixed and labeled for podocalyxin (PDCX, red). GFP-Rab14 is enriched in the cytoplasm between the nucleus and AMIS. DAPI labels the nucleus (blue). (B) shRNA mediated knock-down of Rab14 results in the development of several AMIS domains. Control cells have a single PDCX domain (red) that overlaps partially with E-cadherin (green). Rab14 knock down results in multiple distinct PDCX-positive domains. (C) The tight junction protein cingulin is mis-targeted after Rab14 knockdown. Cell pairs were labeled 16 h after plating with antibodies against PDCX (red) and cingulin (green). In control cells, cingulin localizes at the cell:cell interface (arrows). After Rab14 knockdown, cingulin is distributed at multiple sites at the interface (arrowheads). (D) Rescue of Rab14 knockdown. Rab14 KD cells were transfected with an shRNA-resistant Rab14-GFP. Expression of Rab14-GFP results in single lumen formation. (E) Quantification of single AMIS pairs after Rab14 KD and rescue. **p < 0.01, NS, not significant. (F) Par3 labeling after Rab14 KD. Par3 is localized to cell:cell contacts in control cells, but is distributed to cytoplasmic puncta after Rab14 KD. Scale bars, 10 μm.