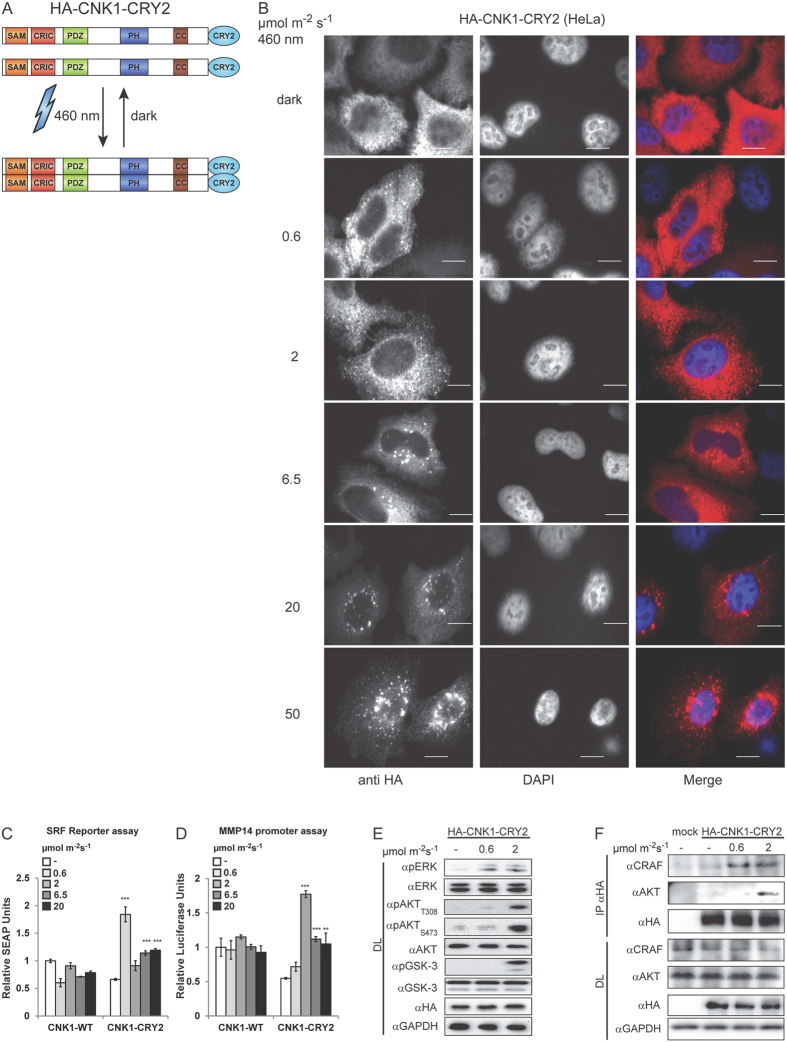
Figure 1. Clustering of CNK1-CRY2 stimulates RAF/ERK and AKT signalling.
(A) Scheme of light-controlled oligomerization of CNK1-CRY2. (B) Immunostaining shows increased clustering of HA-CNK1-CRY2 with increased light intensity at 460 nm. Left: anti-HA antibody for HA-CNK1-CRY2, middle: DAPI for nuclear staining, right: merge images, scale bar: 10 μm. (C) HA-CNK1-CRY2 expressing HEK293T cells preferentially activates SRF-dependent reporter upon illumination with 460 nm blue light activity at 0.6 μmol m−2 s−1. N = 3, mean + SEM, two-tailed Students t-test, ***p < 0.001. See Supplementary Figure S8 for control of protein expression. (D) HA-CNK1-CRY2 expressing HEK293T cells preferentially activate MMP14 promoter-dependent reporter gene expression upon illumination with 460 nm blue light activity at 2 μmol m−2 s−1. N = 3, mean + SEM, two-tailed Students t-test, **p < 0.01 ***p < 0.001. See Supplementary Figure S8 for control of protein expression. (E) HA-CNK1-CRY2 activated with 0.6 μmol m−2s−1 for 15 min increased the level of phosphorylated ERK1/2 (pERK) whereas activation with 2 μmol m−2 s−1 additionally increased phosphorylation of AKT (pAKTT308) and of the AKT substrate GSK-3 (pGSK-3S21). (F) Co-precipitation experiments show that CRAF co-precipitates with HA-CNK1-CRY2 upon illumination with 0.6 μmol m−2 s−1 for 15 min and additionally with AKT upon illumination with 2 μmol m−2 s−1; see also Supplementary Figure S2.